Figure 3. Vasoactive agents modulate the assembly/disassembly of N‐cadherin AJs in the wall of SCAs.
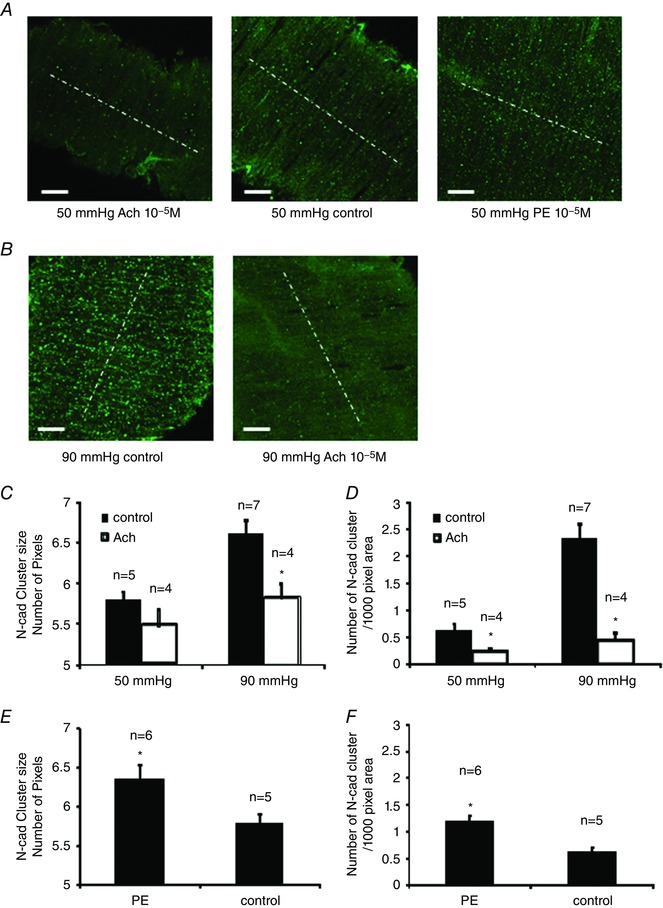
SCAs were pressurized to 50 or 90 mmHg. Control vessels were fixed at 10 min after the vessel pressure was elevated to 90 mmHg or after the vessel tone stabilized at 50 mmHg. For the ACh group, ACh (10−5 m) was added into the bath at 10 min after the vessel tone stabilized at 50 mmHg, or after the vessel pressure was elevated to 90 mmHg. SCAs were fixed within 10 s after the treatment. For PE group, PE (10−5 m) was added into the bath at 10 min after vessel tone stabilized at 50 mmHg. A, N‐cadherin AJs in control vessels and vessels treated with either ACh or PE and vessels were pressurized to 50 mmHg. B, N‐cadherin AJs in control vessels and ACh‐treated vessels pressurized at 90 mmHg. White dashed lines indicate the direction of vessel orientation. C, comparison of N‐cadherin AJ size between control and ACh‐treated groups. D, comparison of N‐cadherin AJ density. E, comparison of N‐cadherin AJ size between control and PE‐treated group. F, comparison of N‐cadherin AJ density between control and PE‐treated group. Pixel size is 0.16 μm 2. One vessel was used for each animal (i.e. the number of vessels n equals the number of animals used for each experiment). * P < 0.05 compared to ACh or PE‐treated groups; n indicates the number of vessels in each group. [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
