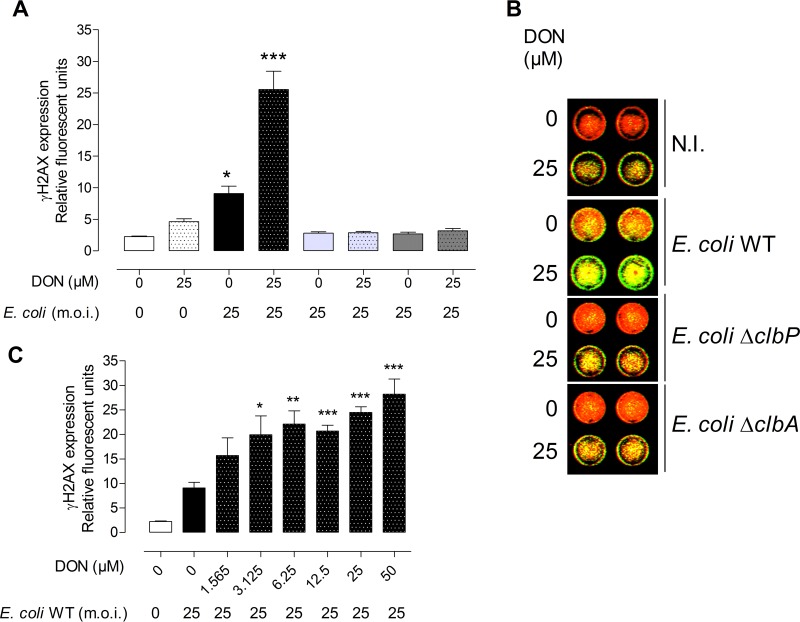
FIG 2 .
Dose-dependent synergistic genotoxicity of DON and E. coli. (A) IEC-6 cells infected for 4 h with E. coli strains producing colibactin (E. coli WT) or not producing colibactin (E. coli ΔclbA and E. coli ΔclbP) (MOI of 25) and coexposed to 25 µM DON 8 h before quantification of γH2AX by in-cell Western (ICW). (B) ICW pictures of IEC-6 cells exposed or not exposed to 25 µM DON and infected (MOI of 25) with E. coli strains producing colibactin (E. coli WT) or not producing colibactin (E. coli ΔclbA or ΔclbP). DNA is artificially colored red, and γH2AX is shown in green. N.I., not infected. (C) IEC-6 cells infected for 4 h with E. coli WT or not infected with E. coli and treated with increasing doses of DON (0 to 50 µM) 8 h before ICW. Control (not treated) cells (white bars) and cells infected with E. coli WT (black bars), E. coli ΔclbP (light gray bars), and E. coli ΔclbA (dark gray bars) are shown. Dotted white, black, light gray, and dark gray bars represent cells exposed to DON and coinfected with different E. coli strains (dotted black, WT; dotted light gray, ΔclbP; dotted dark gray, ΔclbA) or not coinfected with E. coli strains (dotted white). Mean values plus SEM from three independent experiments are shown. Values that are significantly different from the values for cells infected with colibactin-producing E. coli and exposed to DON with all other groups by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple-comparison correction are indicated by asterisks as follows: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.