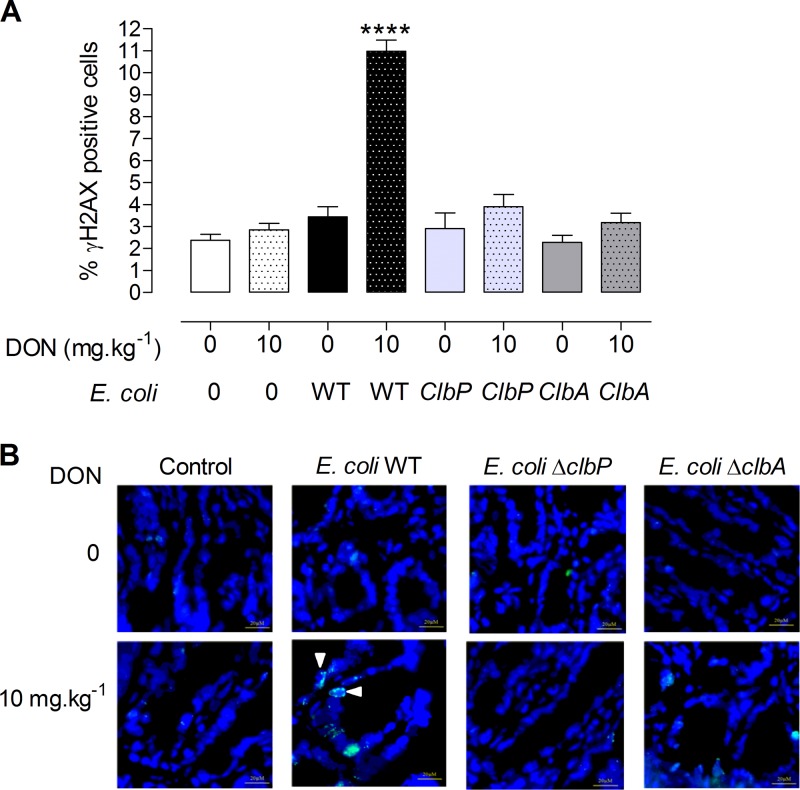
FIG 5 .
DON exacerbates DNA damage in jejunal epithelial cells of animals colonized by colibactin-producing E. coli. Immunofluorescence analysis of the jejunal epithelium of adults (PND 58) colonized since birth by E. coli strains (E. coli WT, E. coli ΔclbA, or E. coli ΔclbP strain) or treated with PBS (control group) and coexposed to a DON-contaminated diet (10 mg ⋅ kg−1) for 4 weeks or not coexposed to a DON-contaminated diet for 4 weeks. (A) Quantification of the percentage of γH2AX-positive cells in jejunal crypts. Mean values plus± SEM are shown (n = 8 to 10). Values that are significantly different (P < 0.0001) by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple-comparison correction are indicated by four asterisks. (B) Representative jejunal frozen sections at PND 58. DNA was stained in blue. γH2AX foci are shown in green. Bars = 10 µM.