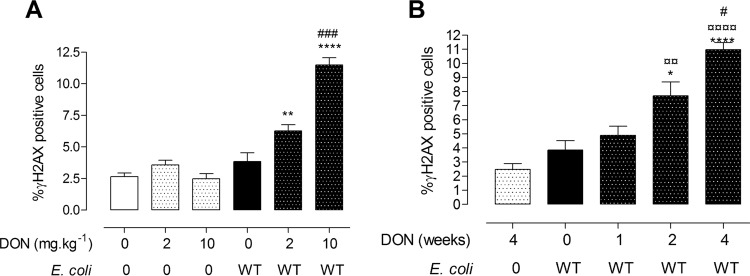
FIG 6 .
DON exacerbates DNA damage in jejunal epithelium in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Immunofluorescence analysis of jejunal epithelium was performed. (A and B) Quantification of γH2AX-positive cells in jejuna of animals exposed to different doses of DON (2 mg ⋅ kg−1 or 10 mg ⋅ kg−1) for 4 weeks and colonized or not since birth with E. coli WT (A) or exposed to DON (10 mg ⋅ kg−1) for 1, 2, or 4 weeks after weaning (B). Mean values plus SEM are shown (n = 6 to 10). Values that are significantly different for control animals (*) or DON-exposed animals (¤) versus E. coli WT-colonized animals exposed to DON by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons are indicated by symbols as follows: *, P < 0.05; ** and ¤¤, P < 0.01; **** and ¤¤¤¤, P < 0.000; ###, P < 0.001, group exposed to 2 mg ⋅ kg−1 of DON versus group exposed to 10 mg ⋅ kg−1 of DON in panel A; #, P < 0.05, E. coli WT-colonized animals exposed to DON for 2 weeks versus E. coli WT-colonized animals exposed to DON for 4 weeks in panel B.