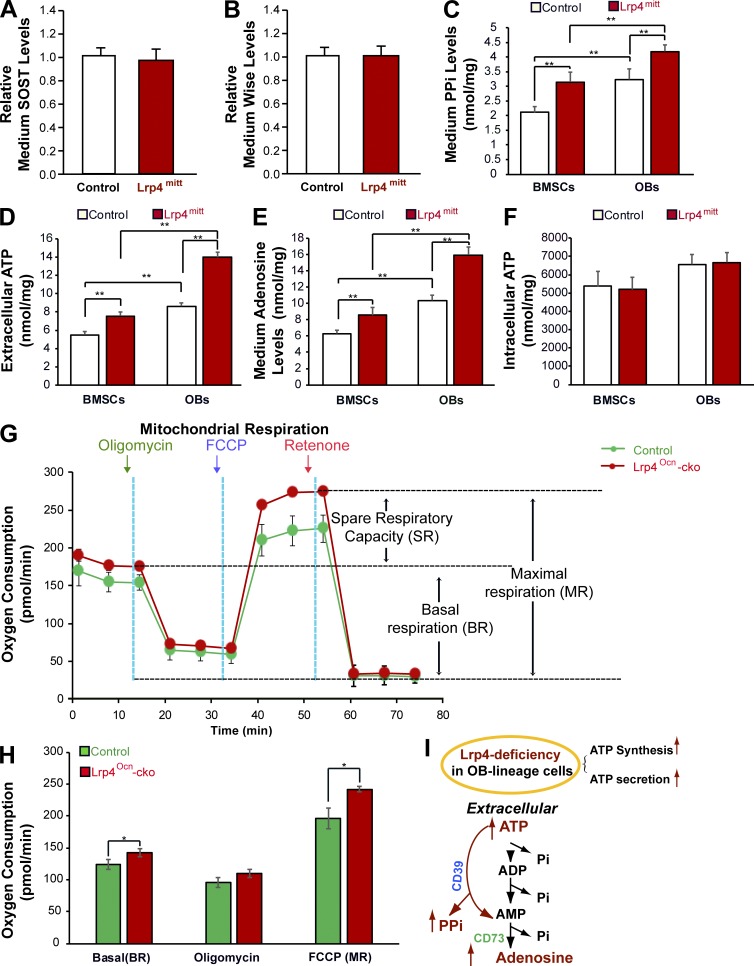
Figure 2.
Increased levels of ATP, PPi, and adenosine in CMs of Lrp4-deficient OB-lineage cells. CMs of Lrp4-deficient BMSCs or OBs were subjected to the indicated analyses as detailed in Materials and methods. (A and B) No changes in SOST or Wise levels were detected. Data represent mean ± SD, n = 3. (C–E) Increased ATP, PPi, and adenosine levels were detected. PPi, ATP, and adenosine levels were measured in the same amounts of culture medium that were collected from the same number of control and mutant cells plated on culture dishes for 3 d. The protein concentrations (in milligrams) of cell lysates were also determined and used to normalize the concentrations (in nanomoles per milliliter) of PPi, ATP, and adenosine. Data represent mean ± SD, n = 3; **, P < 0.001. (F) Intracellular ATP levels in lysates of Lrp4-deficient BMSCs or OBs. Data represent mean ± SD, n = 3; **, P < 0.001. (G and H) An increased oxygen consumption rate (OCR) was detected in Lrp4-deficient OBs by using a Seahorse XF96 analyzer. For validation of the measurements, we used the ATP synthase inhibitor 2 µM oligomycin after recording a basal line, followed by treatment with 3 µM of the pharmaceutical uncoupler FCCP and 1 µM of the complex I inhibitor rotenone. Representative traces of OCRs are indicated in G, and quantification data (mean ± SEM, n = 3; *, P < 0.05) are presented in H. (I) Illustration of a model where Lrp4 deficiency in OB-lineage cells increased ATP secretion, consequently elevating PPi and adenosine levels.