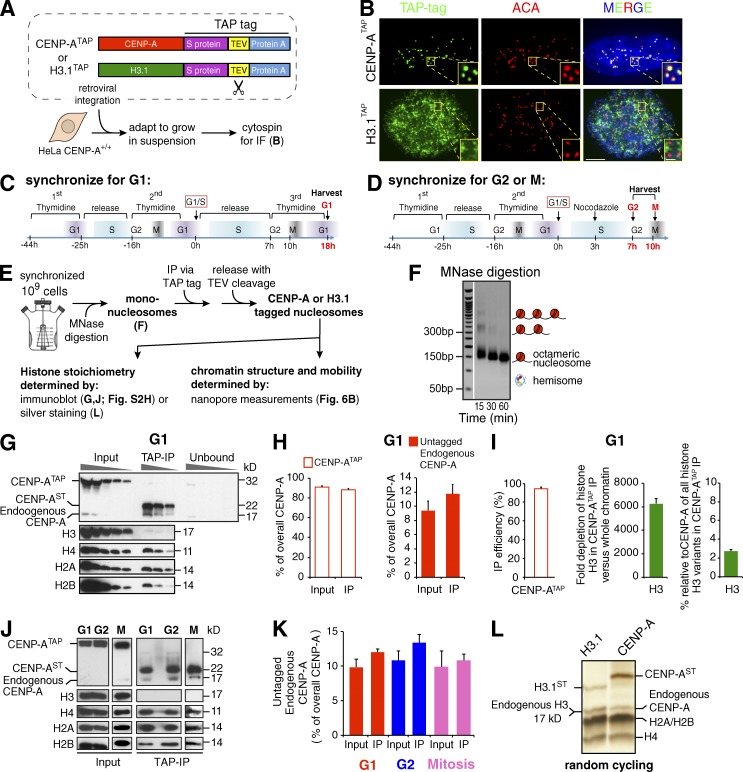
Figure 1.
Purified CENP-A chromatin is a homotypic octamer at G1 and G2 and in mitosis and does not contain H3. (A) HeLa cells stably expressing CENP-ATAP or H3.1TAP (Foltz et al., 2006) were adapted to growth in suspension. The TAP tag includes S protein, TEV protease cleavage site, and protein A. (B) Immunofluorescence (IF) for the TAP-tagged proteins using FITC-IgG. Bar: 5 µm; (inset) 1 µm. (C and D) Double thymidine block synchronization protocol for enriching cells at G1 (C) or at G2 and M phase (D). (E) Experimental design for obtaining mononucleosome pools and TAP-tagged monochromatin particles. (F) Titration of MNase digestion time identifies conditions to generate a pool of bulk soluble mononucleosomes. (G) SDS-PAGE of serial 1:2 dilutions of input, immunoprecipitation, and unbound fractions of affinity-purified CENP-ATAP at G1. (H) Quantification of CENP-ATAP and untagged endogenous CENP-A levels in the input and immunoprecipitation of the blot shown in G, after correcting for the CENP-A fraction that passes through the immunoblot membrane as shown in Fig. S2 (B and C). n = 3 from three independent loadings in the gel shown in G. Error bars represent SEM. (I, left) Efficiency of CENP-ATAP recovery in the immunoprecipitation shown in G. (I, middle) Fold depletion of histone H3 after CENP-ATAP immunoprecipitation. (I, right) Percentage of histone H3 relative to CENP-A in the CENP-ATAP immunoprecipitate. For each panel, n = 3 from three independent loadings in the gel shown in G. Error bars represent SEM. (J) Purified CENP-ATAP monochromatin particles from G1, G2, and M synchronized cells run on SDS-PAGE and blotted for the different histones. (K) Quantification of untagged endogenous CENP-A levels in the input and immunoprecipitation of the blot shown in J. n = 2 from two independent replicates. Error bars represent SEM. (L) Silver-stained SDS-PAGE of purified H3.1TAP and CENP-ATAP monochromatin particles from random cycling cells reveals all four histones at comparable levels.