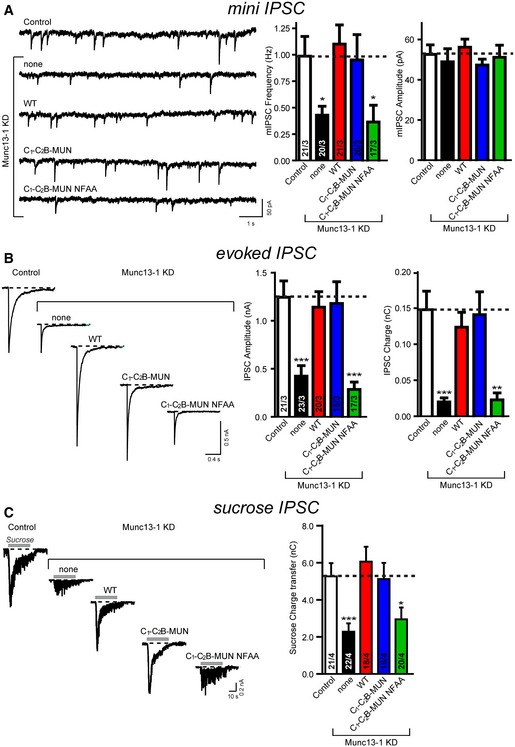
Sample traces (left) and summary graphs (right) of mIPSCs recorded in WT hippocampal neurons that were infected with a control lentivirus (Control) or a lentivirus expressing only Munc13‐1 shRNAs (none) or Munc13‐1 shRNAs plus either full‐length Munc13‐1 (WT), or the C1‐C2B‐MUN fragment (C1‐C2B‐MUN) or the C1‐C2B‐MUN fragment containing the NFAA (N1128A, F1131A) mutations (C1‐C2B‐MUN NFAA), respectively.
Sample traces (left) and summary graphs (right) of action potential‐evoked IPSCs recorded in the infected neuronal cultures described in panel (A).
Sample traces (left) and summary graphs (right) of IPSCs evoked by 0.5 M sucrose, recorded in the infected neuronal cultures described in panel (A).
Data information: Shown are means ± SEM; numbers of cells/independent cultures analyzed are listed in the bars. Statistical assessments were performed by Student's
t‐test comparing each condition to control (*
P < 0.05; **
P < 0.01; ***
P < 0.001).