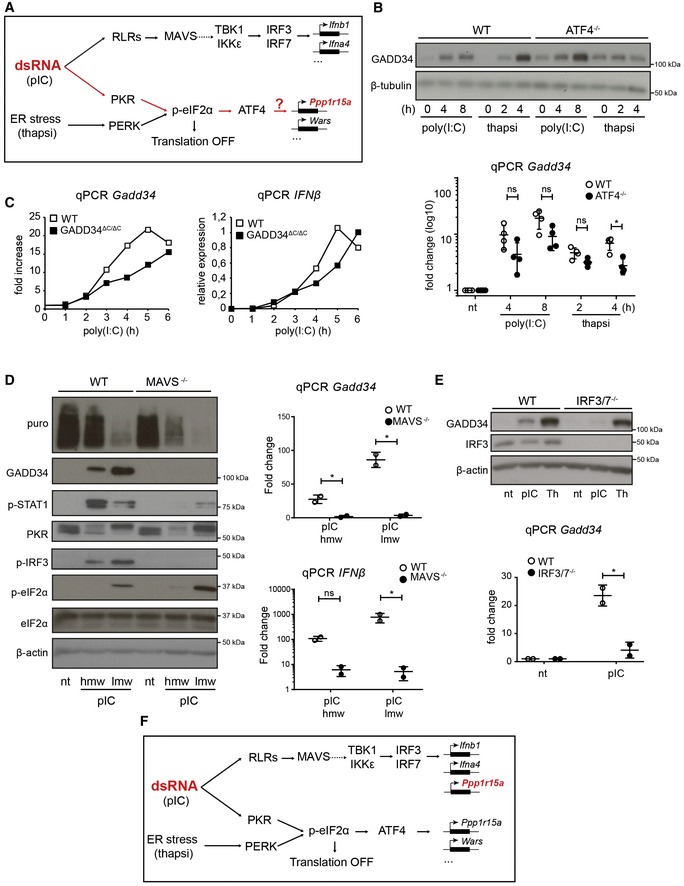
Schematic representation of known signaling pathways involved during dsRNA response and the UPR. Two distinct pathways are triggered in the cytosol of infected cells: RIG‐I‐like receptors (RLRs) detect dsRNA and trigger IRF3 activation via MAVS, while PKR stimulation leads to protein translation inhibition and ATF4‐dependent gene transcription (e.g., GADD34), as observed after PERK activation during thapsigargin‐induced ER stress.
WT and ATF4−/− MEFs were treated with HMW poly(I:C) for 4 h and 8 h, or with thapsigargin (thapsi) for 2 h and 4 h. Expression of GADD34 was analyzed by immunoblot and by qPCR (mean ± SD of five independent experiments). Tubulin is shown as a loading control for immunoblot.
WT and GADD34ΔC/ΔC MEFs were stimulated with LMW poly(I:C). GADD34 and IFNB mRNA expression was monitored by qPCR for 6 h after dsRNA delivery.
WT and MAVS−/− MEFs were analyzed by immunoblot (left) and by qPCR (right panels) after stimulation with poly(I:C) (pIC). Protein synthesis was determined using puromycin labeling followed by immunoblot with the anti‐puromycin mAb. GADD34, p‐STAT1, PKR, p‐IRF3, eIF2α, and p‐eIF2α levels were monitored by immunoblot. Actin is shown as a loading control. Fold increase compared to non‐treated cells in normalized mRNA levels. Each point represents result of one independent experiment.
GADD34 expression was determined by immunoblot and by qPCR in WT and IRF3/7−/− MEFs after HMW poly(I:C) or thapsigargin (Th) treatment. qPCR are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments (“nt” stands for “not treated”).
Schematic representation of predicted signaling pathways involved during dsRNA response and the UPR, according to the results shown in (B–D). GADD34 induction belongs to the primary transcriptional response consecutive to dsRNA sensing and is dependent on IRF3/IRF7 transcription factors, together with IFN‐β.
0.01 (ns: no statistical significance).