Figure 1.
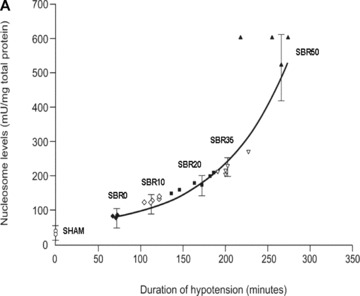
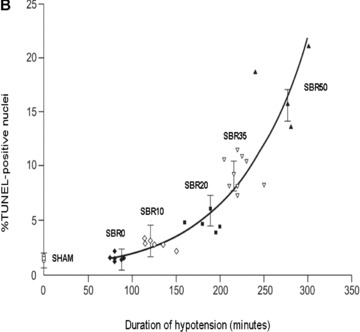
Effect of shock severity on lung apoptosis. Rats were subjected to sham protocol (S) or to T/HS protocol with increasing duration of shock as indicated followed by resuscitation. The lungs were harvested 60 minutes after the start of resuscitation. (A) Nucleosome levels were measured in protein extracts of frozen sections of each lung and the results were plotted after correction for total protein as a function of the duration of the hypotensive period for each animal. Curve fitting was performed and the best‐fitting curve is shown; nucleosome levels increased with the duration of hypotension (Pearson correlation coefficient = 0.764, p < 0.0001). (B) Sections of paraformaldehyde‐fixed lung were stained using the TUNEL assay and TUNEL‐positive nuclei were counted. Data shown represent the percentage of TUNEL‐positive nuclei in 20 random 1,000× fields. Curve fitting was performed and the best‐fitting curve is shown; the percentage of TUNEL‐positive nuclei increased with the duration of hypotension (Pearson correlation coefficient = 0.866, p < 0.0001).
