Figure 1. Idelalisib induces p53-independent PUMA induction in colon cancer cells.
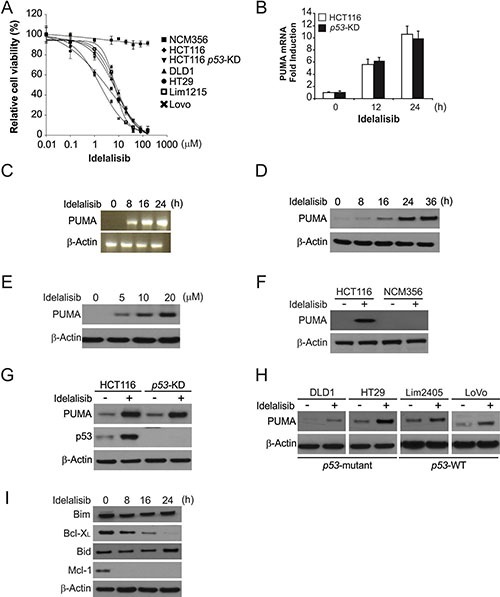
(A) Indicated cell lines were treated with different concentrations of idelalisib for 72 hours. Cell proliferation was determined by MTS assay. Results were expressed as means ± SD of three independent experiments. (B) Parental and p53-KD HCT116 cells were treated with idelalisib at indicated time point. PUMA mRNA induction by idelalisib was analyzed by real-time reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR), with β-actin as a control. (C) HCT116 cells were treated with 10 μmol/L idelalisib at indicated time point. Total RNA was extracted, and PUMA mRNA expression was analyzed by semiquantitive reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR). β-actin was used as a control. (D) HCT116 cells were treated with 10 μmol/L idelalisib at indicated time point. PUMA expression was analyzed by Western blotting. (E) HCT116 cells were treated with idelalisib at indicated concentration for 24 hours. PUMA expression was analyzed by Western blotting. (F) HCT116 and NCM356 cells were treated with 10 μmol/L idelalisib for 24 hours. PUMA expression was analyzed by Western blotting. (G) Parental and p53-KD HCT116 cells were treated with 10 μmol/L idelalisib for 24 hours. PUMA expression was analyzed by Western blotting. (H) Indicated colon cancer cell lines with different p53 status were treated with 10 μmol/L idelalisib for 24 hours. PUMA expression was analyzed by Western blotting. (I) HCT116 cells treated with 10 μmol/L idelalisib at indicated time point. The expression of indicated Bcl-2 family members was analyzed by Western blotting.
