Figure 3. p65 mediates idelalisib induced PUMA induction.
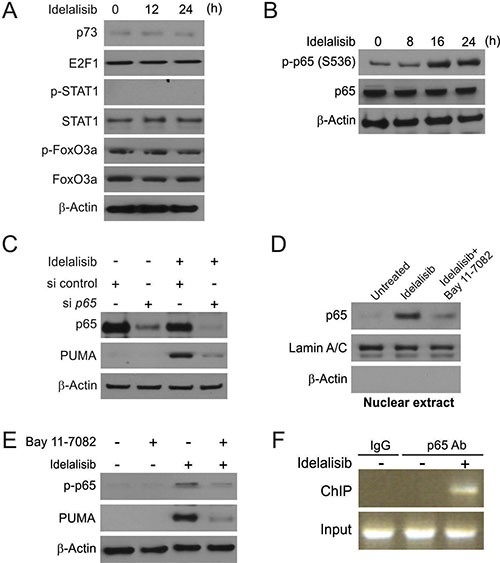
(A) p53-KD HCT116 cells were treated with 10 μmol/L idelalisib at indicated time point. p73, E2F1, p-STAT1, STAT1, p-FoxO3a and FoxO3a expression was analyzed by Western blotting. (B) HCT116 cells were treated with 10 μmol/L idelalisib at indicated time point. p-p65 (S536) and p65 expression was analyzed by Western blotting. (C) HCT116 cells were transfected with either a control scrambled siRNA or a p65 siRNA for 24 hours, and then treated with 10 μmol/L idelalisib for 24 hours. p65 and PUMA expression was analyzed by Western blotting. (D) HCT116 cells were pretreated with 10 μmol/L BAY11-7082 for 1 hour, and then with 10 μmol/L idelalisib for 24 hours. Nuclear fractions were isolated from cells and analyzed for p65 expression by Western blotting. Lamin A/C and β-actin were used as controls for loading and fractionation. (E) HCT116 cells were pretreated with 10 μmol/L BAY11-7082 for 1 hour, and then with 10 μmol/L idelalisib for 24 hours. p-p65 (S536) and PUMA expression was analyzed by Western blotting. (F) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) was performed using anti-p65 antibody on HCT116 cells following idelalisib treatment for 12 hours. ChIP with the control IgG was used as a control. PCR was carried out using primers surrounding the p65 binding sites in the PUMA promoter.
