Figure 6. PUMA mediates the antitumor effects of idelalisib in a xenograft model.
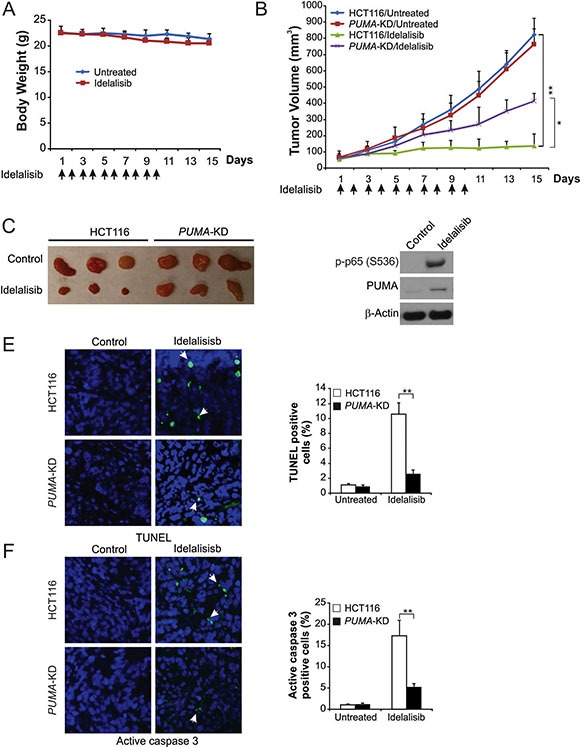
(A) Nude mice were treated with 30 mg/kg idelalisib for 10 consecutive days. Body weight at indicated time points was measured. Arrows indicate idelalisib injection. (B) Nude mice were injected s.c. with 4 × 106 parental and PUMA-KD HCT116 cells. After 1 week, mice were treated with 30 mg/kg idelalisib or buffer for 10 consecutive days. Tumor volume at indicated time points after treatment was calculated and plotted (n = 6 in each group). Arrows indicate idelalisib injection. (C) Representative tumors at the end of the experiment in (B). (D) Parental HCT116 xenograft tumors were treated with 30 mg/kg idelalisib or the control buffer as in (B) for 4 consecutive days. p-p65 (S536) and PUMA in representative tumors were analyzed by Western blotting. (E) Paraffin-embedded sections of tumor tissues from mice treated as in (B) were analyzed by TUNEL staining. Left, representative TUNEL staining pictures; Right, TUNEL-positive cells were counted and plotted. (F) Tissue sections from (E) were analyzed by active caspase 3 staining. Left, representative staining pictures; Right, active caspase 3-positive cells were counted and plotted. Results of (B), (E) and (F) were expressed as means ± SD of 3 independent experiments. **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05.
