Figure 2. Detection analysis by PNA directed PCR clamping of CALR type-1 (DEL) and type-2 (INS) mutations.
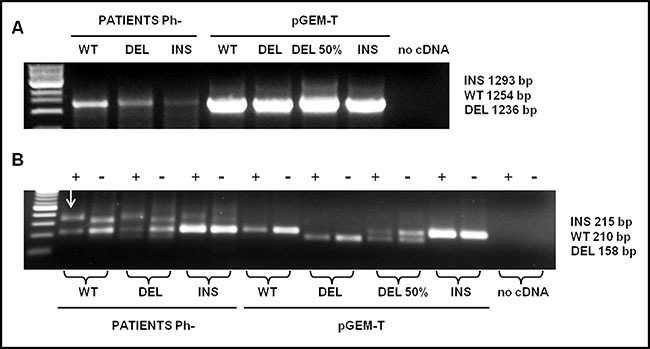
(A) Step I: cDNA amplification of patients with CALR wild-type (WT), type-1 (DEL) and type-2 (INS) mutations. pGEM-T-CALR wild-type (WT), pGEM-T-CALR type-1 mut (DEL), pGEM-T-CALR type-1 mut 50% vs. wild-type (DEL 50%) and pGEM-CALR type-2 mut (INS) were used as PCR positive control. 5 μL of each amplifier were loaded on 1% Agarose-TBE 1x gel with 5 μg/mL ethidium bromide (EtBr) and run at 120 V for 30 minutes. (B) Step II: PCR amplification of a small area of CALR gene, containing type-1 and type-2 mutations, was carried-out in absence (−) or in presence (+) of PNA probe. The plasmids amplified in the step I were used, in a dilution of 1:100, in the step II in order to interpret the results, 10 μL of each amplifier were loaded on 2% Agarose-TBE 1x gel with 5μg/mL EtBr and run at 100 V for 30 minutes and than at 65 V for 15 minutes. The arrow indicates the non-specific band present in the amplified of patients.
