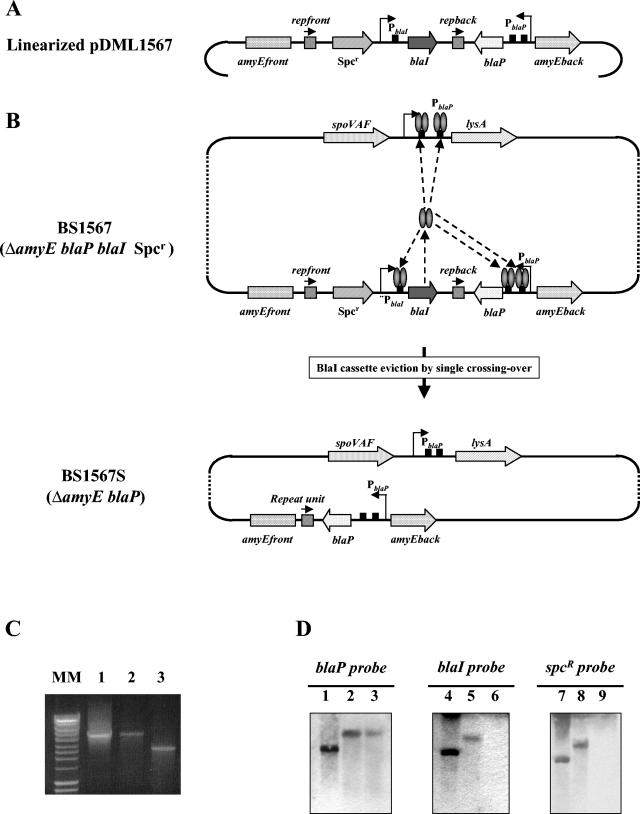
FIG. 4.
Construction and characterization of BS1567 and BS1567S strains by PCR and Southern blot analyses. (A) Linearized pDML1567 plasmid carrying blaP, the BlaI cassette, and amyEfront and amyEback sequences. PblaI and PblaP are the native promoters of the B. licheniformis 749/I blaI and blaP genes, respectively. Rectangles correspond to the operator DNA sequences recognized by the BlaI repressor. (B) The pDML1567 insert was introduced by double crossover into the BS1541 strain to generate the BS1567 strain. This strain exhibits lysine auxotrophydue to the presence of the BlaI repressor that negatively controls the expression of the lysA gene. For the same reason, the expression of the blaP gene is very low. The eviction of the BlaI cassette by single crossover between the two direct repeat unit sequences (repfront and repback) was achieved as described in the legend to Fig. 3 to generate the BS1567S (ΔamyE blaP) strain. (C) PCR amplifications of amyE. The amplified fragments were generated with primers amyEfront and amyEback and were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. Lanes 1, 2, and 3 correspond to PCR experiments carried out with BS1567 chromosomal DNA, plasmid pDML1567, and BS1567S chromosomal DNA as template, respectively. MM, molecular size marker (Smart ladder; Eurogentec). (D) Southern Blot analysis of the BglII-digested chromosomal DNA from BS1567 (lanes 2, 5, and 8) and BS1567S (lanes 3, 6, and 9). Linearized pDML1567 (lanes 1, 4, and 7) was used as positive control. blaP, blaI, and Spcr probes were generated by PCR with the following primers pairs as amplimers: BlaP+/BlaP−, BlaINdeI/BlaIEcoRI, and Spc+/Spc−. pDML1567 was the DNA template. For more details see Materials and Methods.