Figure 3. Combined performance of mucins and associated O-glycans for discriminating colorectal polyp subtypes.
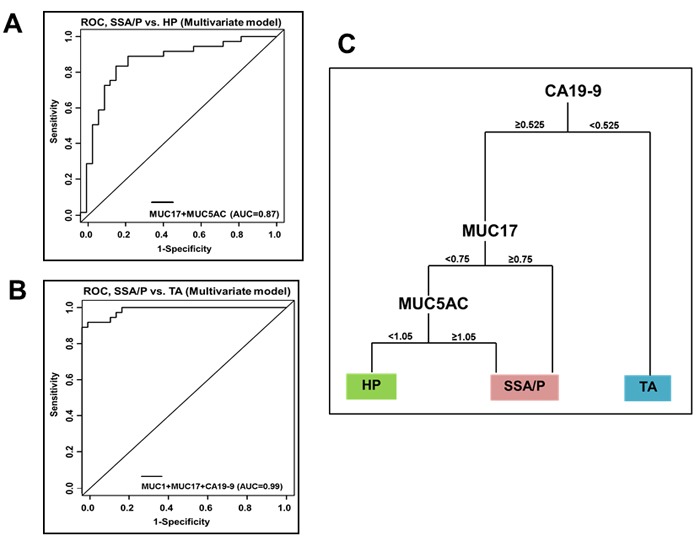
The combined utility of significantly altered mucins and O-glycans as markers for differential identification of polyp subtypes was evaluated utilizing multivariate regression models in conjunction with ROC curve based analysis. A. ROC curves representing diagnostic potential of combinatorial panels of mucins and associated O-glycans for differentiating SSA/P from HP. MUC17+MUC5AC combination differentiated SSA/P from HP with the AUC of 0.87. The model has 83% accuracy (60/72) in predicting SSA/P vs. HP. B. MUC1 and MUC17+CA19-9 combination differentiated SSA/P from TA with the AUC of 0.99. the model has 95% accuracy (71/75) in predicting SSA/P vs. TA. C. Decision tree based model to accurately define the combined diagnostic efficacy of mucins and associated O-glycans for polyp stratification. The panel of three markers CA19-9/MUC17/MUC5AC differentiated precancerous polyps (SSA/P and TA) from benign polyps (HP). Polyp sections having H-Score < 0.525 for CA19-9 predicts the presence of TA. For tissues sections having H-Score ≥ 0.525 for CA19-9, and H-score ≥ 0.75 for transmembrane mucin MUC17 the lesion is likely to be SSA/P. In cases where MUC17 H-score is < 0.75, and MUC5AC H-score is ≥ 1.05, then SSA/P is predicted and if MUC5AC H-score < 1.05, then HP is predicted. The tree based model has 79% accuracy (85/108) in predicting all 3 groups simultaneously.HP: hyperplastic polyps; SSA/P: sessile serrated adenoma/polyps; TA: tubular adenoma.
