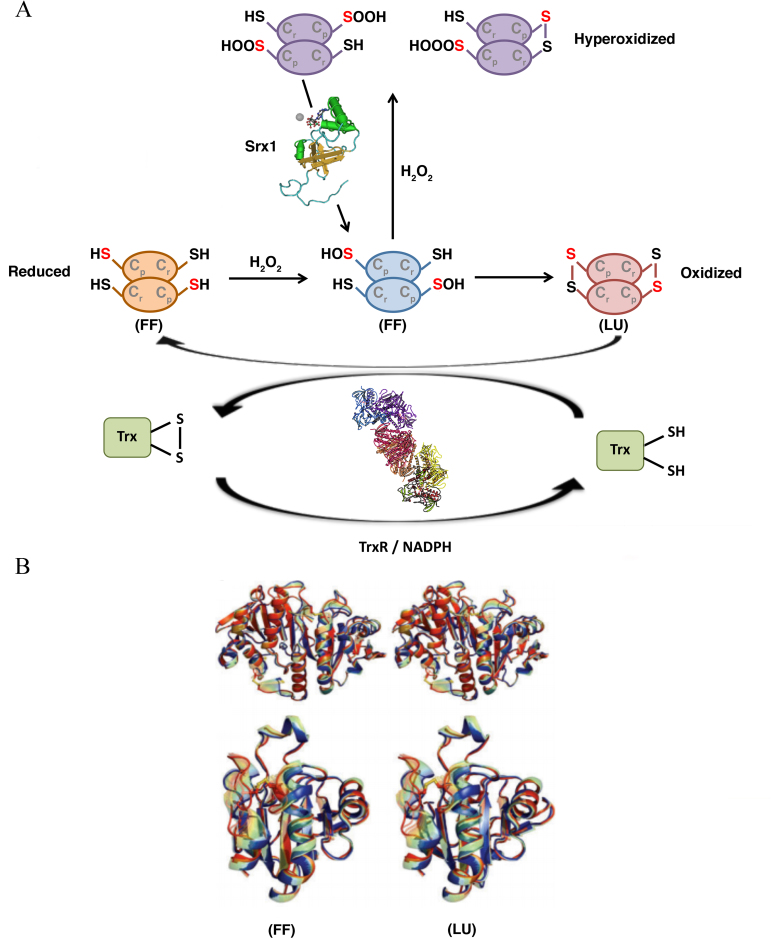
Figure 4.
Catalytic mechanism of typical 2-Cys PRDXa. (A) PRDXs switch from an FF conformation, in which Cp reacts with the peroxide, to an LU conformation, in which the Cp is exposed and forms a disulfide bridge with the Cr residue. The thiol groups are converted into sulfenic acid (−S-OH) and form disulfide bonds with other thiol groups (−SS-) (oxidized status-LU conformation). At high peroxide concentrations, the sulfenic acid intermediate is overoxidized to sulfinic acid (−SOOH) or even sulfonic acid (−SOOOH), causing the inactivation of the enzyme (hyperoxidized status). (B) Stereo-view of the interpolated structural changes shown in rainbow colors between the FF (blue) and LU (red) conformations for a representative of Prx1 subfamily (upper) and Prx5 subfamily (lower). PRDX, peroxiredoxin; Srx1 sulfiredoxin 1, Trx, thioredoxin; TrxR, thioredoxin reductase; FF, fully folded; LU, locally unfolded.