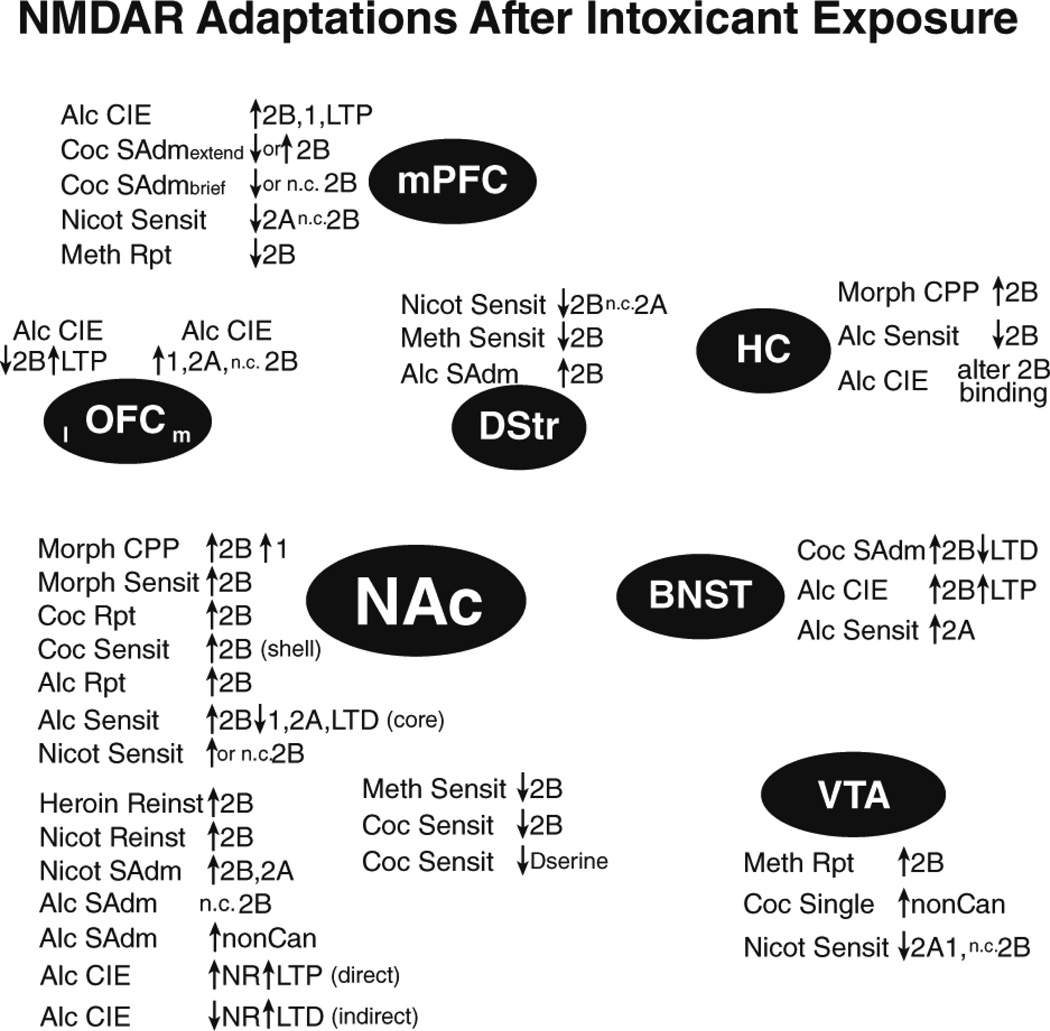
Figure 1.
NMDAR adaptations after exposure to addictive intoxicants. Summary of NMDAR adaptations observed after passive or active intoxicant exposure. Adaptations are grouped near the brain region they have been reported within. List of abbreviations: 1: GluN1; 2A: GluN2A; 2B: GluN2B; ADE: alcohol deprivation effect; Alc: alcohol; bottle: alcohol intake from a bottle; brief: brief daily access; CIE: chronic intermittent ethanol exposure; Coc: cocaine; Compul: compulsion-like; direct: direct-pathway (DA1R–containing) cells; Dser: d-serine; extend: extended daily access; indirect: indirect-pathway (DA2R–or adenosine-2-receptor-containing) cells; KO: knockout; l: lateral; m: medial; Meth: methamphetamine; Morph: morphine; n.c. no change; Nicot: nicotine; nonCan: non-canonical NMDARs; NR: NMDAR; operant: operant intake; Reinst: reinstatement; Reward: acute reward; Rpt: repeated; SAdm: self-administration; Sensit: sensitization; Single: single exposure.