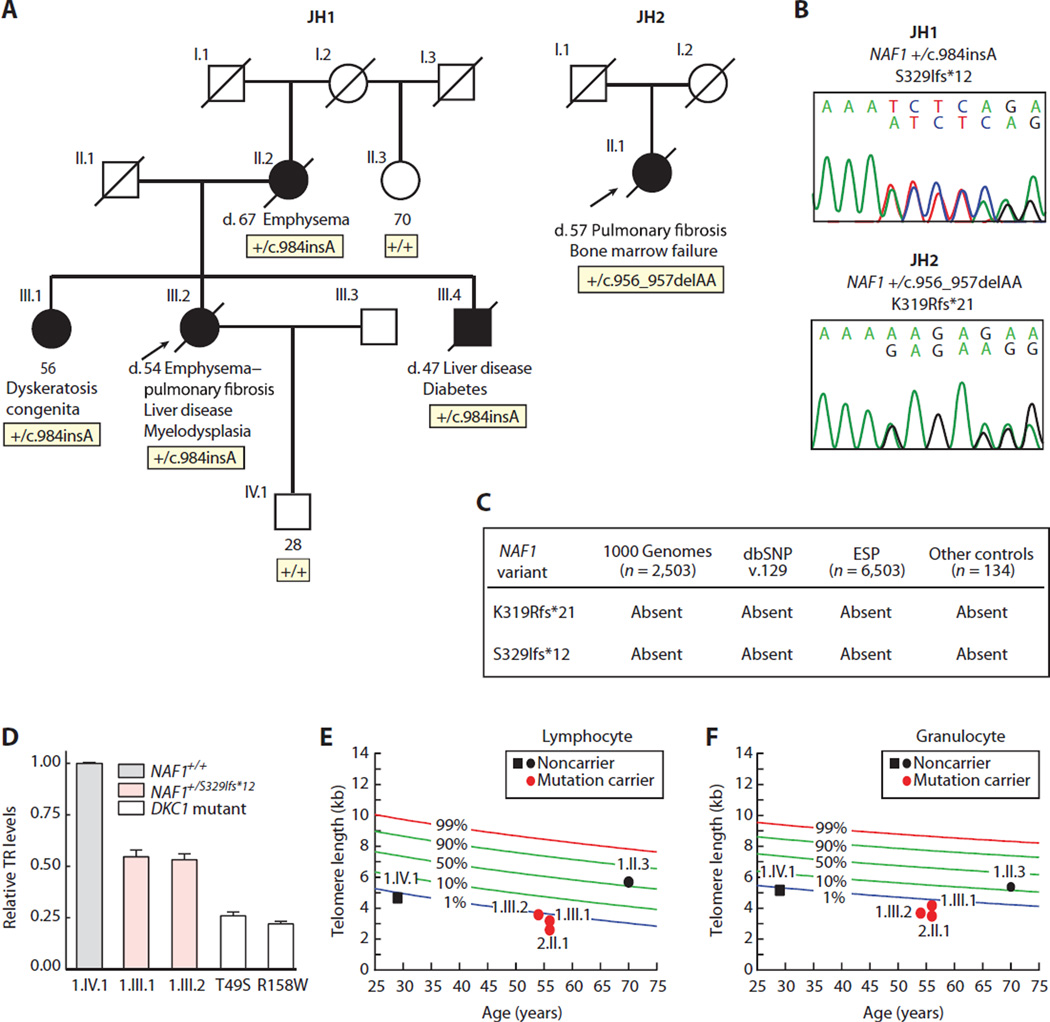
Fig. 1. Rare NAF1 variants segregate with short telomere disease phenotypes and low TR levels.
(A) Pedigrees of cases identified in a Johns Hopkins–based Registry (JH1 and JH2) with NAF1 genotypes shown below the individuals sequenced. NLS, nuclear localization signal. (B) Chromatograms of rare NAF1 variants by Sanger sequencing. (C) NAF1 variants are absent in public databases, as well as additional controls that we sequenced. dbSNP, Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Database; ESP, Exome Sequencing Project. (D) TR levels by qRT-PCR in LCLs with pedigree identifiers referring to (A). TR levels from DKC1 mutation carriers serve as a positive control, and the DKC1 missense mutations are annotated below. Means are from three separate RNA isolations and experiments, and the error bars represent SEM. (E and F) Age-adjusted telomere length in lymphocytes and granulocytes, respectively, measured by flow cytometry and fluorescence in situ hybridization (flow-FISH), with pedigree identifiers corresponding to individuals in (A). The nomogram was constructed from 192 healthy controls, and the calculated percentiles are labeled.