Fig. 2. Fault-normal cross section A–A′ detailing seismicity within 5 km.
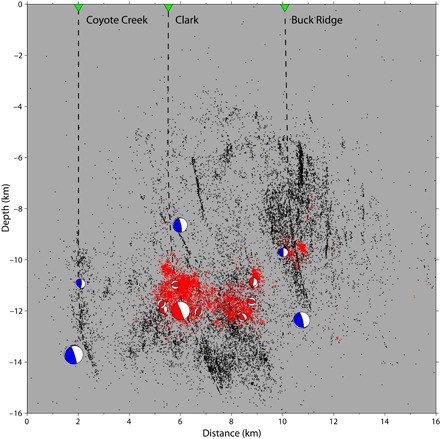
Black dots denote the regional network relocated solutions (20), whereas red dots indicate the detected aftershocks of the 2016 Borrego Springs earthquake. Red focal mechanisms correspond to aftershocks with M > 3.0, whereas blue focal mechanisms on the CL, CC, and BR faults are from the 2008 Mw 4.06, 2010 Mw 5.4, and 2013 Mw 4.7 sequences, respectively. The 2016 main shock is indicated by the largest red focal mechanism. All focal mechanisms shown are rear hemisphere projections. The interpreted locations of the CC, CL, and BR fault planes are shown as dashed lines and dip nearly 70° below 10 km. A change in dip must occur at around 10 to 13 km in order for the faults to meet with the surface expression (green triangles). In the regions off the main faults, there are damage zones with intense distributed seismicity that includes persistently dipping lineations.
