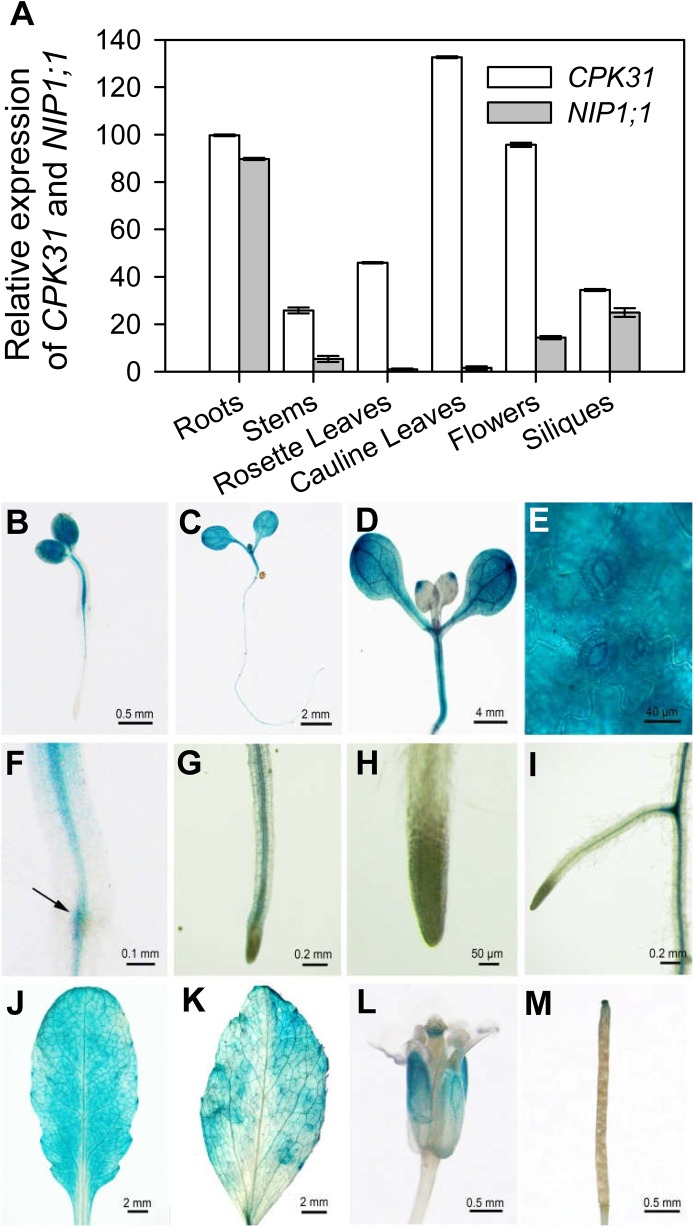
Fig 5. Analysis on tissue expression pattern of CPK31.
(A) Quantification analysis of CPK31 and NIP1;1 transcripts in various organs of the wild-type plants. Total RNA was isolated from various tissues (root, leaf, stem, flower and silique) of 4-week-old wild-type plants (Col-0) grown in soil under long-day conditions. Values were normalized to ACTIN2, and the relative mRNA expression levels were calculated as the ratio of NIP1;1 or CPK31 mRNA level to the NIP1;1 level in rosette leaves of plants (as 1.0). Data are mean ± SD of four replicate experiments. (B-M) Histochemical analysis of CPK31 promoter–GUS expression in transgenic plants. GUS staining in 2-day-old (B), 3-day-old (C), and 7-day-old (D) transgenic seedlings grown on half-strength MS agar plates. The enlarged part of the cotyledon (E), root–hypocotyl junction (F), primary root (G), the tip of primary root (H), and lateral-primary root junction (I) of 7-day-old seedlings. GUS staining in cauline leaf (J), rosette leaf (K), flower (L), and silique (M) of mature CPK31::GUS transgenic plants. To obtain adult plants for staining, 7-day-old seedlings grown on 1/2 MS agar plates were transferred into soil, and samples used for GUS analysis were collected for (J) to (M) on the 21th day after the transfer.