Figure 5. CD82 suppresses fibronectin-induced EMT by attenuating fibronectin-binding integrin signaling cascades including the FAK-Src and ILK pathways.
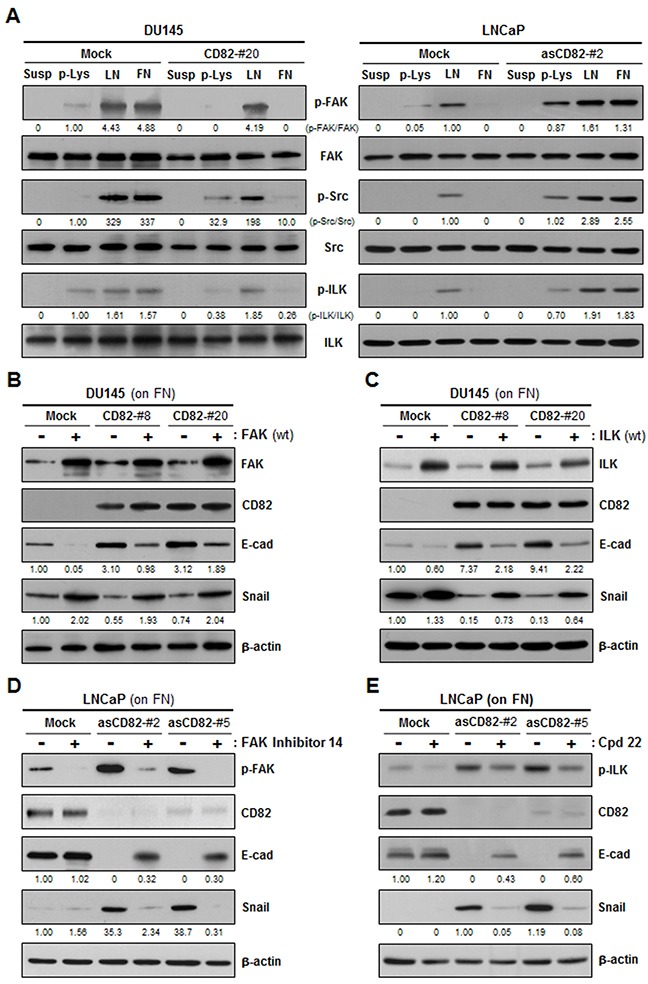
A. DU145 and LNCaP cell transfectant clones were cultured on plates precoated with poly-L(+)-lysine (p-Lys), laminin (LN), or fibronectin (FN) for 8 hours. Phosphorylation levels of FAK, Src, and ILK in the cells in suspension (Susp) and cells grown onto the plates were assessed by immunoblotting analysis using antibodies recognizing phospho-FAK(Tyr-925), phospho-Src(Tyr-416), or phospho-ILK(Thr-173). Shown are representative immunoblots from three separate experiments performed in triplicate. Numbers under the immunoblots indicate the relative band intensity of the phosphorylated protein normalized to the protein level. B, C. DU145 cell transfectant clones grown on FN were transiently transfected with a wild-type FAK (B) or ILK (C) expression construct, and examined for E-cadherin and Snail expression. The protein level was normalized to the loading control (actin) level. D, E. LNCaP cell transfectant clones were pretreated with inhibitors specific to FAK (FAK inhibitor 14) (D) or ILK (Cpd22) (E) at a concentration of 0.1 μM for 2 hours. Cells were cultured on FN-coated plates for 8 hours and then assessed for the protein levels of E-cadherin and Snail as well as the phosphorylation levels of FAK (D) and ILK (E).
