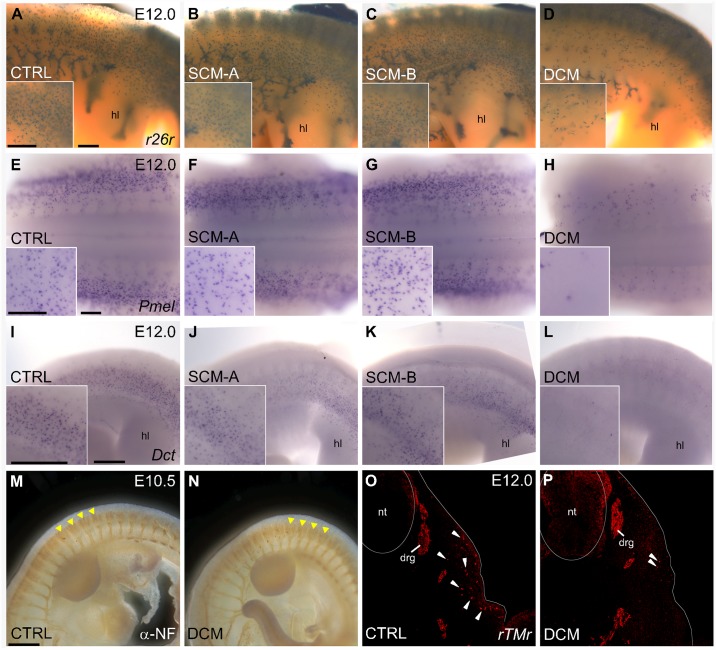
Fig 4. TFAP2A and TFAP2B redundantly regulate murine melanocyte development.
(A-D) Lateral views of E12.0 control (A), Tfap2a SCM (B), Tfap2b SCM (C), or Tfap2a/Tfap2b DCM (D) mouse embryos processed for β-galactosidase (β-gal) staining. β-gal+ cells are a result of recombination of the r26r-allele by the Wnt1-Cre transgene, labeling neural crest cells and derivatives. (E-L) In situ hybridization expression patterns for Pmel (E-H, dorsal views) or Dct (I-L, lateral views) in control (E, I), Tfap2a SCM (F, J), Tfap2b SCM (G, K), or Tfap2a/Tfap2b DCM (H, L) E12.0 mouse embryos. Insets in (A-L) show higher magnification images just above the hindlimb in a similar viewing plane as the low magnification image. (M, N) Lateral views of the trunk processed for ɑ-neurofilament immunoreactivity in an E10.5 control (M) or Tfap2a/Tfap2b DCM (N), revealing developing dorsal root ganglia (a subset labeled with arrowheads). (O, P) Immunofluorescence of cryosections (cross-sectional plane at the level of the hindlimb) of an E12.0 control (O) or Tfap2a/Tfap2b DCM (P), containing a Tomato-reporter (rTMr) allele labeling neural crest cells and derivatives (arrowheads highlight a subset of melanocytes in the ventrolateral pathway). Abbreviations: DCM, double conditional mutant; drg, dorsal root ganglia; hl, hindlimb; nt, neural tube; SCM, single conditional mutant (A = Tfap2a or B = Tfap2b). Scale bars = 250μM, except M, N = 500μM.