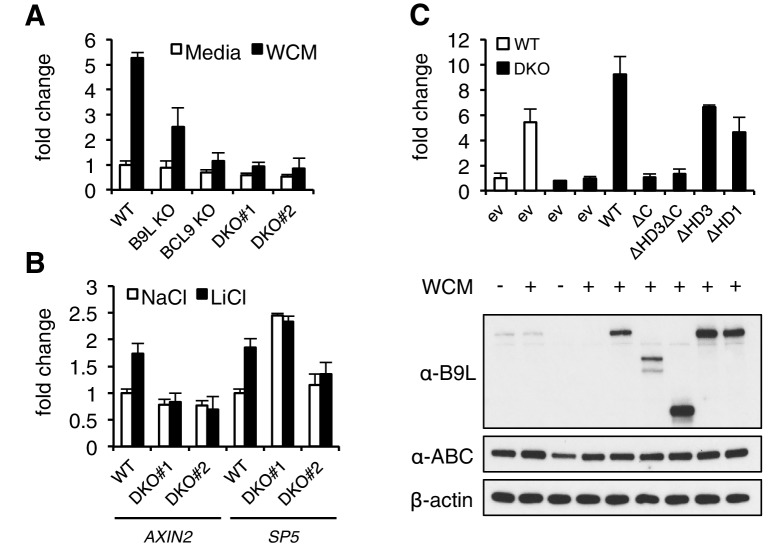
Figure 3. The C-terminus of BCL9/B9L is required for transcriptional Wnt responses in human cells.
(A) SuperTOP assays in wt or KO HEK293T cells lacking BCL9 and/or B9L, as indicated, ±6 hr of Wnt stimulation (WCM, Wnt3a-conditioned-media); mean ± SEM (n = 3 independent experiments). (B) RT-qPCR assays in wt or DKO HEK293T cells, ±6 hr of 20 mM NaCl or LiCl as indicated, revealing relative transcript levels of AXIN2 or SP5; values were normalized to TBP (internal control), and are shown as mean ± SEM relative to unstimulated wt controls (set to 1); note that the uninduced levels of SP5 were unusually high in one of the two DKO clones, but neither of the DKO clones showed Wnt-inducible SP5. (C) SuperTOP assays in wt or DKO HEK293T cells as in (A), 24 hr after transfection with wt and mutant B9L as indicated (below, corresponding Western blots; α-ABC, active unphosphorylated β-catenin); ev, empty vector control.
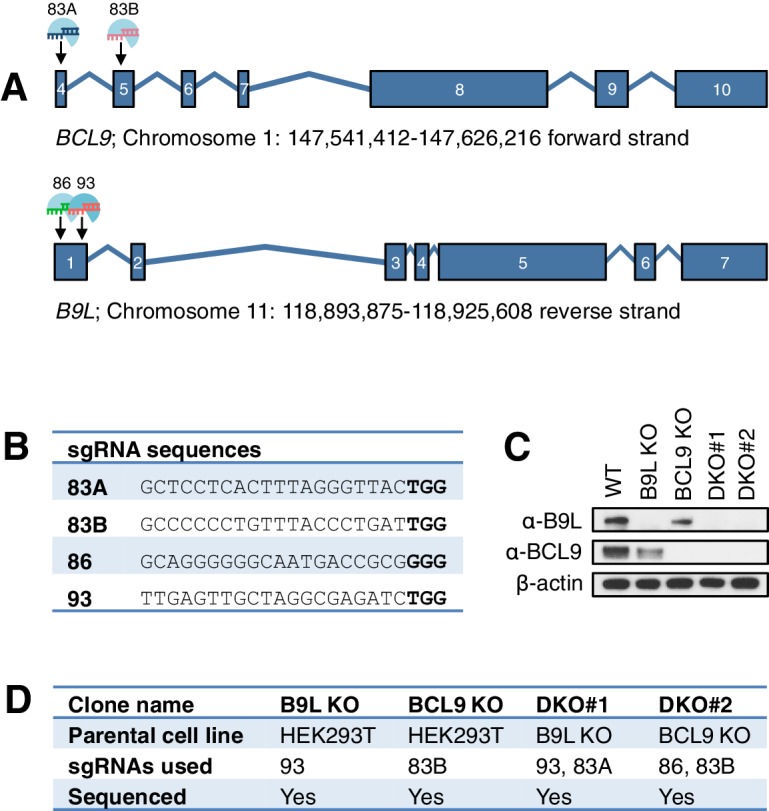
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. CRISPR/Cas9-based gene editing strategies for BCL9 and B9L in HEK293T cells.