Figure 7. Schematic model of molecular mechanisms underlying tumor-promoting effect of N-cadherin in thyroid cancer.
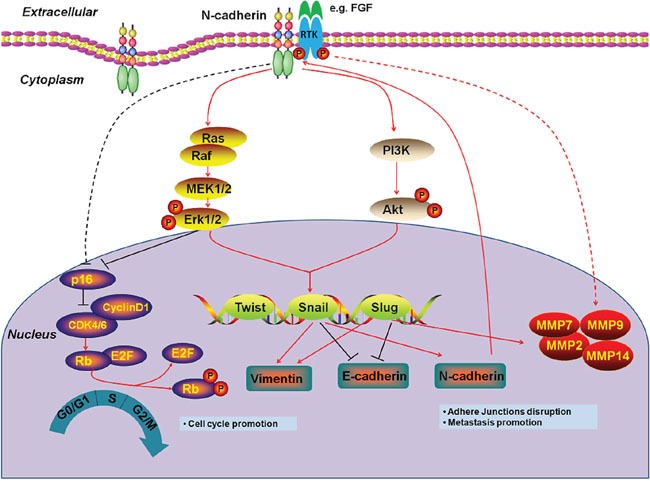
Increased expression of N-cadherin stabilizes certain growth factor receptors (e.g., FGFR) to activate their downstream signaling pathways including MAPK/Erk and PI3K/Akt pathways through interacting with their extracellular domains in thyroid cancer cells. The activation of MAPK/Erk and PI3K/Akt cascades upregulates the EMT regulatory factors such as Twist, Snail and Slug. These transcription factors then promotes the process of EMT through transcriptionally regulating the EMT-associated markers such as E-cadherin, Vimentin and N-cadherin and MMPs production. Newly synthesized N-cadherin is subsequently translocated to cellular membrane where it plays a tumor-promoting function through interacting with some growth factor receptors. In addition, N-cadherinalso promotes cell cycle progression through modulating p16/Rb pathway via Erk-dependent or –independent mechanisms.
