Figure 1.
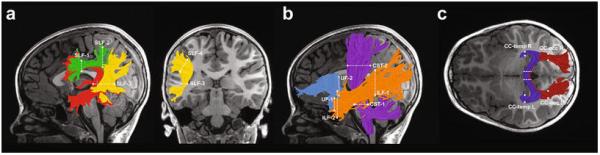
Tractography of 6 bilateral cerebral white matter tracts and 2 posterior segments of the corpus callosum. Left hemisphere cerebral tract renderings are displayed on a mid-sagittal T1 image from a representative child in the Reader group. Right hemisphere tract renderings not shown. Dashed lines represent the location of the regions of interest (ROIs) used to segment each cerebral tract from the whole-brain fiber group. Panel a illustrates the following subdivisions of the superior longitudinal fasciculus (SLF): Arcuate Fasciculus (Arc) = red, anterior SLF (aSLF) = green, and posterior SLF (pSLF) = yellow. Fibers belonging to the Arc were required to pass between SLF-1 and SLF-3. Fibers belonging to the aSLF were required to pass between SLF-1 and SLF-2. Fibers belonging to the pSLF were required to pass between SLF-3 and SLF-4 but not SLF-1. Panel b illustrates the following tracts: Inferior Longitudinal Fasciculus (ILF) = orange; Corticospinal Tract (CST) = purple; Uncinate Fasciculus (UF) = light blue. Panel c illustrates the following subdivisions of the corpus callosum (CC): temporal (CCTemp) = dark blue and occipital (CC-Occ) = dark red.
