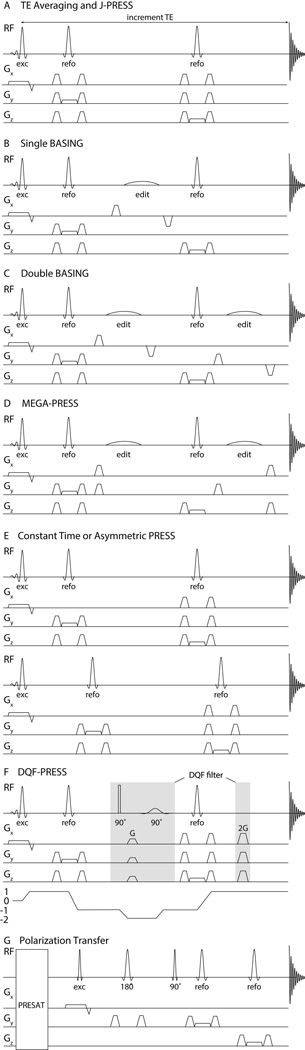
Figure 1.
Pulse sequences that are used to edit the spectrum. A. TE-averaging: the echo time is varied during the acquisition. The typical PRESS localization scheme is used with gradients applied during the 90 excitation pulse and the two 180 refocussing pulses. B. Single BASING: a single frequency-selective editing pulse is placed between the two refocusing pulses. C. Dual Basing: in half of the transients, two frequency-selective editing pulses are applied, one after each refocusing pulse. These editing pulses refocus the evolution of selected couplings. In the remaining half of the transients, these pulses are not applied (pulse sequence not shown) such that in the subtraction spectrum, overlapping larger resonances are removed, revealing only the spins impacted by the editing pulses. D. MEGA (MEscher-GArwood): Similar to the dual BASING scheme, a pair of frequency-selective editing pulses refocus the evolution of the coupling in half of the transients, the ‘On’ condition. The difference between the subspectra with and without the refocusing pulses subtracts the overlapping metabolites to reveal the metabolite of interest. E. Asymmetric PRESS: Two spectra with same TE but different interpulse delays are acquired. Timings are optimized to maximize differences in the modulation of strongly coupled spins, so their signals are enhanced in the difference spectrum, and resonances from singlets are removed. F. Example of a double quantum filter experiment and the associated coherence transfer pathway. The double-quantum coherence is formed by the excitation pulse, first refocusing pulse and an additional 90° pulse. Subsequently, the 90° frequency-selective pulses convert the desired double quantum signals into observable coherence. G. Polarization transfer: First, signals in the spectral range of interest are pre-saturated (PRESAT). Signal is then excited on a spin outside the saturated range and transfered to a coupled partner. Within the saturated range, only signal that arises from such coherence transfer give detectable signals in the acquired spectrum. Coherence transfer is achieved by the pulse marked 90°.