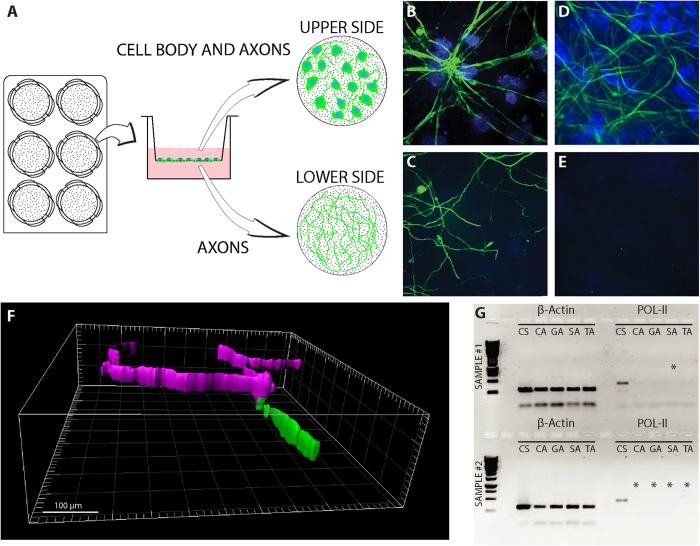
Figure 1. Separation of axons from cell bodies.
(A) Schematic description of the separation system. Embryonic motor neurons are cultured in a 6-well plate fitted with PET membrane inserts. As neurons grow, axons cross through membrane pores to the lower side of the membrane, allowing the harvest of axons independently of cell bodies, which are located on the upper side. (B–E) Immunofluorescent staining of neurons on PET membrane: Upper (B,D) and lower (C,E) parts of a membrane before (B,C) and after (D,E) harvesting axons. Cell nuclei are shown in blue (DAPI). Axons are shown in green (NFH). Scale bar is 20 μm. (F) 3D rendering of immunofluorescent staining of neurons on PET membrane showing two axons converging and passing through a single membrane pore. The upper membrane fraction is shown in purple and the lower membrane fraction in green. (G) A representative image of two cDNA gel electrophoresis separation quality-control runs; β-actin was used as a positive control and POL-II as a marker for separation. Asterisks indicate samples that passed separation QC and were used for deep sequencing. Sample annotation [XY]: X: C, G, S, T = Control, GFP, SOD, TDP samples, respectively. Y: S = Soma, A = Axon.