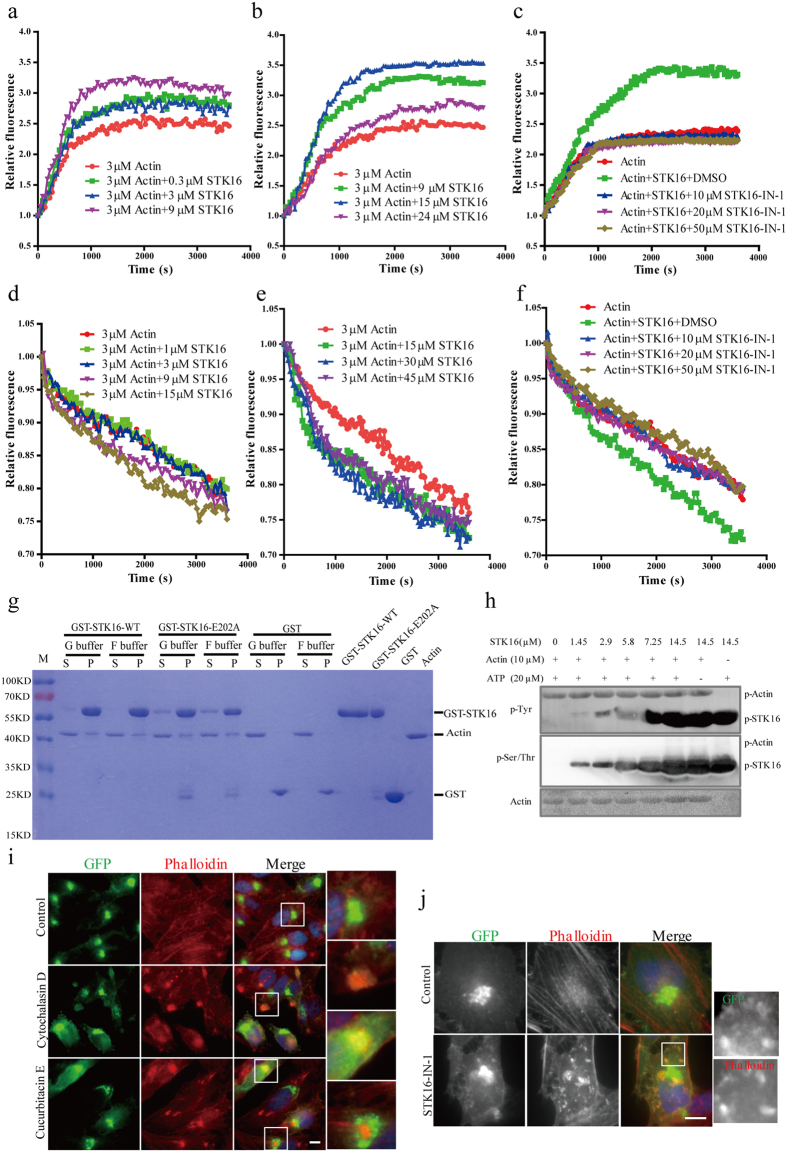
Figure 4. STK16 directly binds to actin and regulates actin dynamics in vitro in a concentration- and kinase activity -dependent way.
(a,b) STK16 protein stimulates actin polymerization, and peaked at 5:1 ratio (STK16: actin). 3 μM G-actin mixed with 10% pyrene-actin was incubated with 0.3, 3 and 9 μM (a), or 9, 15, and 24 μM (b) STK16 protein. Polymerization was induced by 10× polymerization buffer. (c) The kinase activity of STK16 protein is critical for its stimulation effect on actin polymerization. 10 μM, 20 μM, and 50 μM STK16-IN-1 were incubated with 3 μM G-actin mixed with 10% pyrene-actin and 15 μM STK16 protein, respectively. (d,e) STK16 affects actin depolymerization at higher concentrations. F-actin polymerized from 3 μM G-actin mixed with 10% pyrene-actin was incubated with 1, 3, 9 and 15 μM (d), or 15, 30, and 45 μM (e) STK16 protein. Depolymerization was induced by adding 2 μM Latrunculin A. (f) The kinase activity of STK16 protein plays a role in actin depolymerization. 10 μM, 20 μM, and 50 μM STK16-IN-1 were incubated with F-actin polymerized from 3 μM G-actin mixed with 10% pyrene-actin and 30 μM STK16 protein, respectively. (g) GST pull-down experiments show that both WT and E202A STK16 bind to actin directly. GST, GST-STK16-WT or GST-STK16-E202A protein and actin were at 5:1 ratio in G-buffer or F-buffer, respectively. “S”, Supernatant; “P”, Pellet. (h) 0, 1.45, 2.9, 5.8, 7.25, 14.5 μM STK16 protein was incubated with 10 μM Actin. The phospho-Tyrosine, phospho-Serine/Threonine, and actin antibodies were used in western blots. (i) STK16 binds to actin puncta after actin depolymerization in vivo. HeLa-STK16-GFP-FLAG-WT cells treated with DMSO, 100 nM Cytochalasin D, and 10 nM Cucurbitacin E for 4 hours were stained for anti-GFP antibody (green) and fluorescence-labeled phalloidin (red). (j) STK16 partly distributes from its original localization to cytoplasm and binds with actin puncta after its kinase activity is inhibited by STK16-IN-1. HeLa-STK16-GFP-FLAG-WT cells were treated with DMSO and 50 μM STK16-IN-1 for 2 hours. Experiments were repeated 2–3 times and representative images are shown. Scale bar, 10 μm.