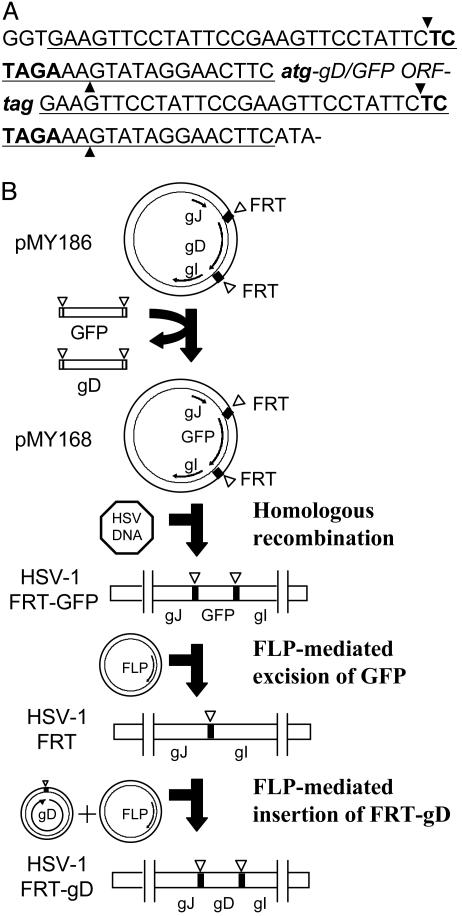
Fig. 1.
Use of FLP recombinase and FRT sites to perform precise gene replacements in the HSV-1 genome and to generate HSV-1/FRT-gD. (A) Sequence of the FRT sites in pMY186 and pMY168. The 47-bp FRT site (underlined) contains an XbaI site (bold type). Strand cleavage by FLP recombinase occurs at the positions marked by arrowheads. The FRT sites are located immediately upstream and downstream of the start and stop codons (lowercase italic bold type) of the gD or GFP ORFs. (B) Plasmids containing the gD ORF (pMY186) or GFP ORF (pMY168) bounded by FRT sites and by regions of the HSV-1 genome normally found upstream and downstream of the gD ORF were constructed as described in Materials and Methods. The gD ORF in the HSV-1 genome was replaced by the GFP ORF, bounded by FRT sites by homologous recombination, to generate HSV-1/FRT-GFP. HSV-1/FRT was obtained after cotransfection of cells with the HSV-1/FRT-GFP genome and a plasmid expressing FLP recombinase, which excised the GFP ORF. HSV-1/FRT-gD was obtained by site-directed recombination after cotransfection of VD60 cells with the HSV-1/FRT genome, a plasmid expressing FLP recombinase and the WT gD ORF with ends joined by a single 47-bp FRT site.