Figure 6.
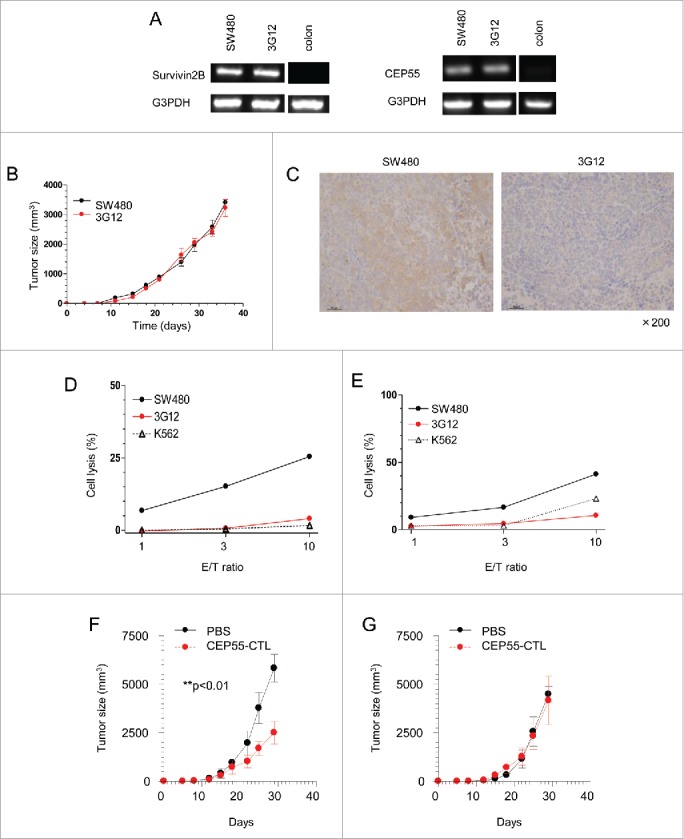
Tapasin deficiency leads to escape from TAA-specific CTL-mediated cytotoxicity. A and B, Survivin and cep55 gene expression in SW480, 3G12 and a normal colon tissue. (B) Tumor growth rates of SW480 and 3G12. 1 × 105 SW480 or 3G12 cells were subcutaneously injected into NSG mice. The x-axis and the y-axis indicate days after injection and the sizes of tumors, respectively. Tumor volume was calculated as follows: volume = xy2/2. Data are shown as mean + SEM (n = 3). (C) Immunohistochemistry of dissected tumors 36 d after injection. Formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissues were stained with tapasin mAb (magnification x200). D and E, LDH cytotoxicity assay of the CTLs specific to the survivin 2B epitope and the cep55 epitope presented by HLA-A24. LDH releases from indicated target cells cultured with survivin 2B-specific CTL clones (D) and cep55-specific CTL clones (E) were measured. The x-axis and y-axis indicate effector/target (E/T) ratios and % target cell lysis, respectively. Data are representatives of three independent experiments. F and G, The adoptive transfer of cep55-specific CTLs and tumor rejection in vivo. SW480 (F) and 3G12 (G) cells were subcutaneously injected into NSG mice. The mice received the adoptive transfer of PBS (black) or 2 × 106 cep55-specific CTLs (red) 10 and 17 d after tumor injection. The x-axis indicates days after tumor injection. Data are shown as mean + SD (n = 3). p-values were calculated using a two-tailed t-test (**p < 0.01).
