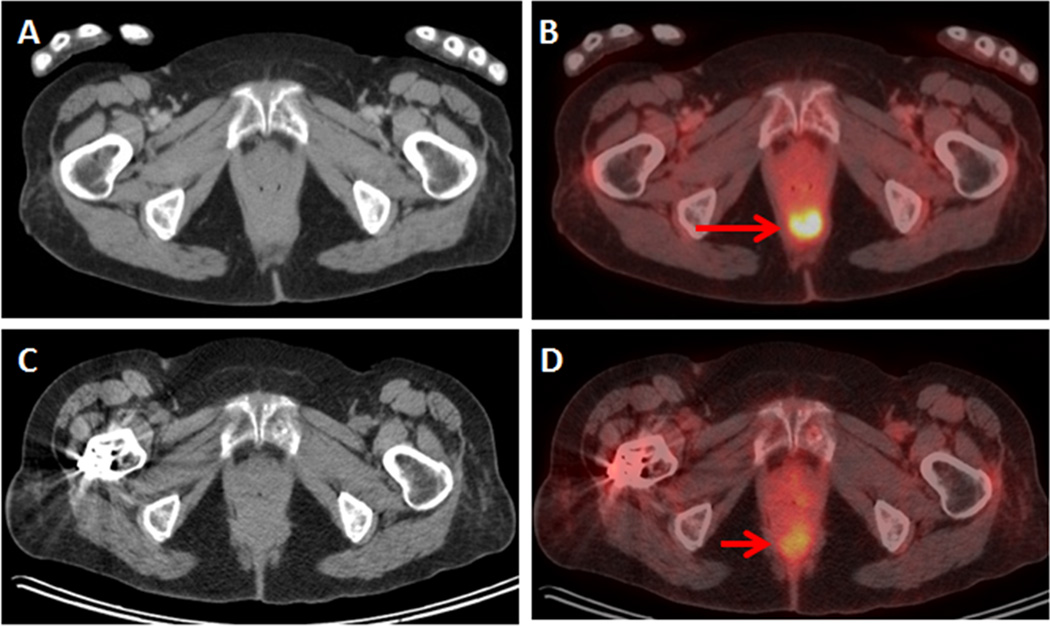
Figure 2.
73-year-old woman with ovarian cancer. FDG PET/CT was ordered for staging. (A) Axial CT and (B) axial fused PET/CT demonstrate an FDG-avid focus in the inferior pelvis, without corresponding mass on CT. This was called malignant on the initial report. Second opinion report called this finding benign, noting the FDG-avid focus localized to the distal rectum and represented the rectal sphincter. Follow-up FDG PET/CT with (C) axial CT and (D) axial fused PET/CT demonstrated resolution of the FDG-avid focus, consistent with benign rectal sphincter avidity.