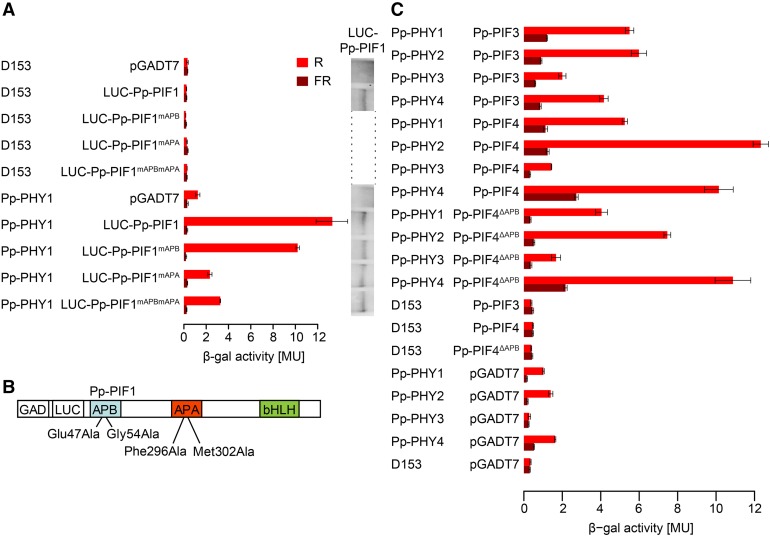
Figure 4.
Interaction of LUC-Pp-PIF1 with Light-Activated Pp-PHY1 in Yeast Requires the APA Motif.
(A) Full-length Pp-PIF1 fused to LUC interacts with P. patens PHY1 in a light-dependent manner. This interaction is abolished by mutations in the Pp-PIF1 APA motif. GAD plasmids (pGADT7) containing the coding sequence for Pp-PIF1 and mutated versions of Pp-PIF1 (Pp-PIF1mAPB, Pp-PIF1mAPA, and Pp-PIF1mAPBmAPA), respectively, fused to the GAL4 activation domain (GAD) and the coding sequence of luciferase (LUC) were used in yeast two-hybrid assays with GBD plasmids (D153) containing the coding sequence for Pp-PHY1 fused to the GAL4 DNA binding domain (GBD). Phytochromes were converted into the Pfr or Pr form by irradiating yeast cultures for 5 min with R (12 µmol m−2 s−1) or FR (12 µmol m−2 s−1) light. The β-galactosidase activity was measured after an additional incubation in the dark for 4 h. MU, Miller units. Bars indicate the mean of three biological replicates (i.e., three independent cultures were grown; each culture was measured in triplicate); error bars represent 95% confidence interval. The protein abundance of the wild type and mutated Pp-PIF1 in yeast was analyzed by immunoblot using an antibody specific to LUC. For complete immunoblot analyses of LUC-Pp-PIF1 and Pp-PHY protein abundance, refer to Supplemental Figure 8.
(B) Mutations inserted in Pp-PIF1 APB and APA motifs are shown schematically.
(C) Pp-PIF3, Pp-PIF4, and Pp-PIF4ΔAPB interact with Pp-PHY1, 2, 3, and 4 in a light-dependent manner. GAD-Pp-PIF3, 4, and 4ΔAPB versions and Pp-PHYs fused to GBD were used in yeast two-hybrid assays as described in (A).