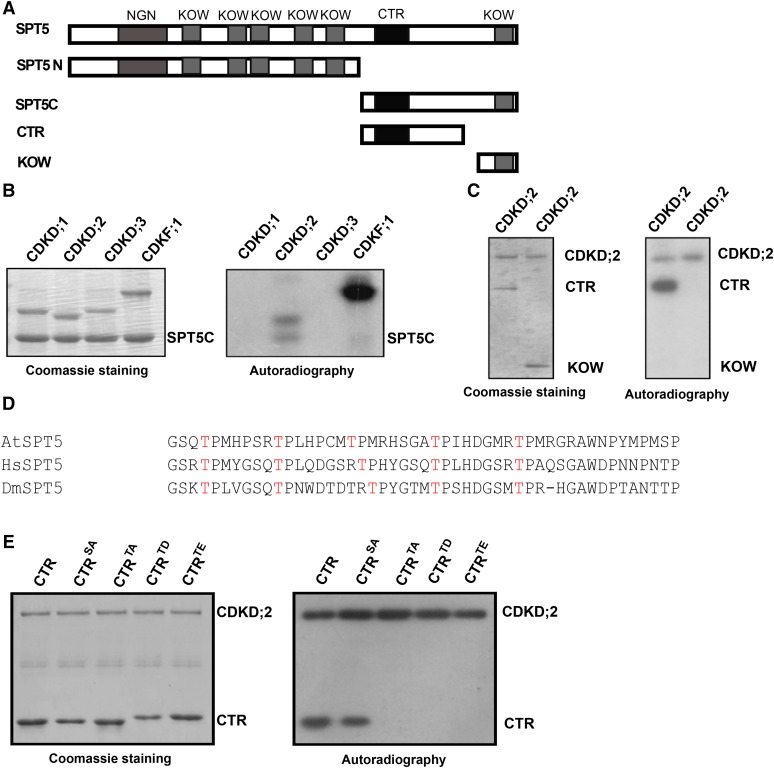
Figure 2.
CDKD;2 Phosphorylates SPT5.
(A) Different regions of SPT5 containing the indicated domains (NGN, KOW, and CTR) tested in the phosphorylation and yeast two-hybrid analyses are shown.
(B) CDKD;2 phosphorylates the C terminus of SPT5. The ability of CDKD;1, CDKD;2, CDKD;3, and CDKF;1 to phosphorylate the C terminus of SPT5 was assessed.
(C) CDKD;2 phosphorylates the CTR of SPT5. The positions of the CTR and KOW domains are indicated on the right.
(D) Alignment of the CTR domain with other closely related SPT5s using ClustalW. The amino acid sequences of Arabidopsis SPT5 (744–792 amino acids), human SPT5 (772–829 amino acids), and Drosophila Spt5 (822–869 amino acids). The conserved threonines are indicated in red.
(E) The activity and specificity of CDKD;2 kinase assessed using different substrates. Substrates contain the SPT5 CTR fused with His and are either wild-type (CTR) or have all serines converted into alanine (CTRSA) or all threonines converted into alanine (CTRTA), aspartic acid (CTRTD), or glutamic acid (CTRTE).
For (B), (C), and (E), the left panel shows the Coomassie blue-stained gel. The positions of the different CDKs and SPT5 fragments are indicated on the right. Autoradiography (right panel) indicates any kinase activity and its specificity.