Figure 4.
Mutations in CDKD;2 Result in Early Flowering.
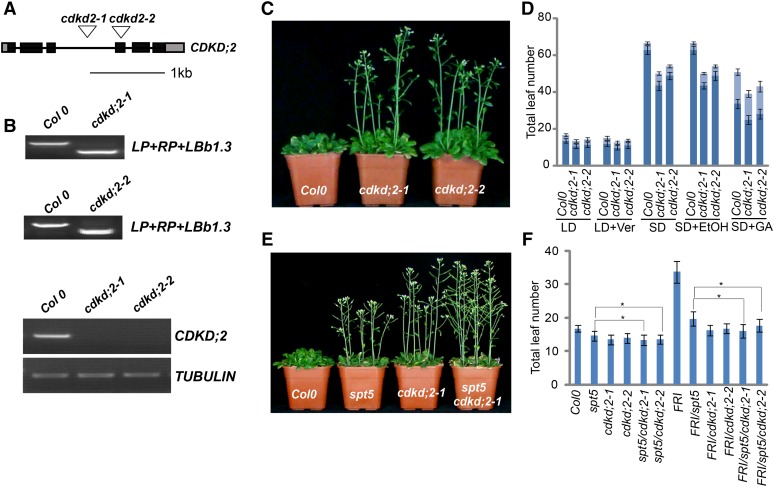
(A) Gene structure of CDKD;2. Boxes represent exons and lines represent introns. T-DNA insertions are indicated with a triangle.
(B) Genotypic and RT-PCR analysis of cdkd;2 mutants. The genotype was analyzed with the left genomic primer (LP), right genomic primer (RP), and primer in the vector (LBb1.3). Genotype analysis is shown in the top and middle panels; transcription is shown in the bottom panel. TUBULIN was used as internal control.
(C) The cdkd;2 mutants exhibit an early-flowering phenotype.
(D) Flowering time of Col-0 and the cdkd;2 mutants under different conditions or treatments. Flowering time was assessed by counting the number of rosette leaves and cauline leaves in bolting plants under a long-day photoperiod (LD), vernalization (LD+Ver), short-day photoperiod (SD), and GA treatment (SD+GA). SD+EtOH (ethanol) treatment was used as a GA treatment control. The rosette leaves are indicated in dark blue and the cauline leaves are indicated in light blue. Values shown are mean number ± sd of rosette and cauline leaves; 40 plants were scored for each line.
(E) Flowering time of Col-0, spt5, cdkd;2-1, and the spt5 cdkd;2-1 double mutant under LD photoperiod.
(F) The leaf number of Col-0, spt5, cdkd;2-1, and spt5 cdkd;2-1 with or without FRI under LD photoperiod. Total leaf number at flowering is shown for each indicated strain; asterisk indicates statistically significant by t test. Values shown are mean number ± sd of total leaves; 40 plants were scored for each line.