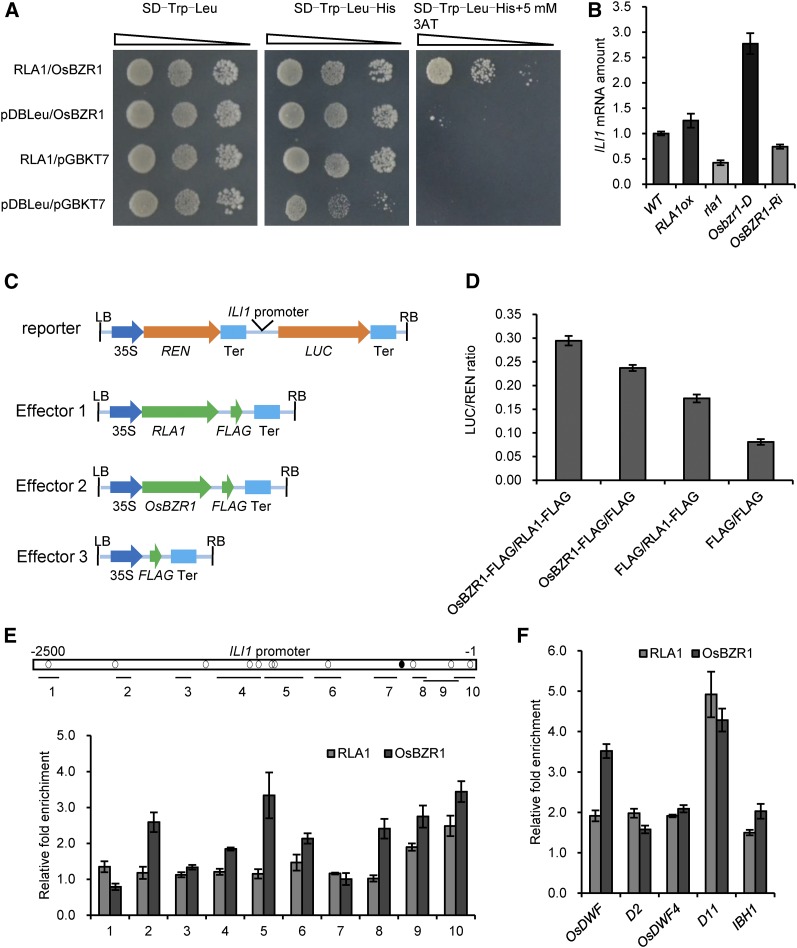
Figure 6.
RLA1 Works with OsBZR1 and Enhances Its Transcriptional Activity.
(A) RLA1 enhances OsBZR1 transcriptional activity in yeast. OsBZR1-pGBKT7 and RLA1-pDBLeu were cotransformed in yeast.
(B) The transcript level of ILI1 in the wild type, RLA1ox, rla1, Osbzr1-D, and OsBZR1-Ri. The transcript level in the wild type was defined as “1.” Data are means ± se (n = 3).
(C) Schematic diagrams of the dual-luciferase reporter and effector constructs. The firefly luciferase (LUC) gene driven by the ILI1 promoter was used as the reporter. The Renilla luciferase (REN) reporter gene was controlled by the CaMV promoter (35S) and terminator (Ter). For the effectors, RLA1 and OsBZR1 were fused with FLAG.
(D) Transient gene expression assays in N. benthamiana mesophyll cells. The LUC reporter gene was cotransfected with OsBZR1-FLAG, RLA1-FLAG, or both. Data are means ± se (n = 3).
(E) ChIP assays on binding of RLA1 and OsBZR1 to the ILI1 promoter. Open box shows promoter region of ILI1, black circles show BR response element motifs, and white circles show putative E-box motifs. Regions analyzed by quantitative PCR are shown by short lines marked with numbers (1 to 10). The fold enrichment represents binding efficiency ratio of antibody/no antibody. Data are means ± se (n = 3).
(F) Binding of RLA1 and OsBZR1 to the promoters of OsDWF, D2, OsDWF4, D11, and IBH1. The fold enrichment represents binding efficiency ratio of antibody/no antibody. Data are means ± se (n = 3).