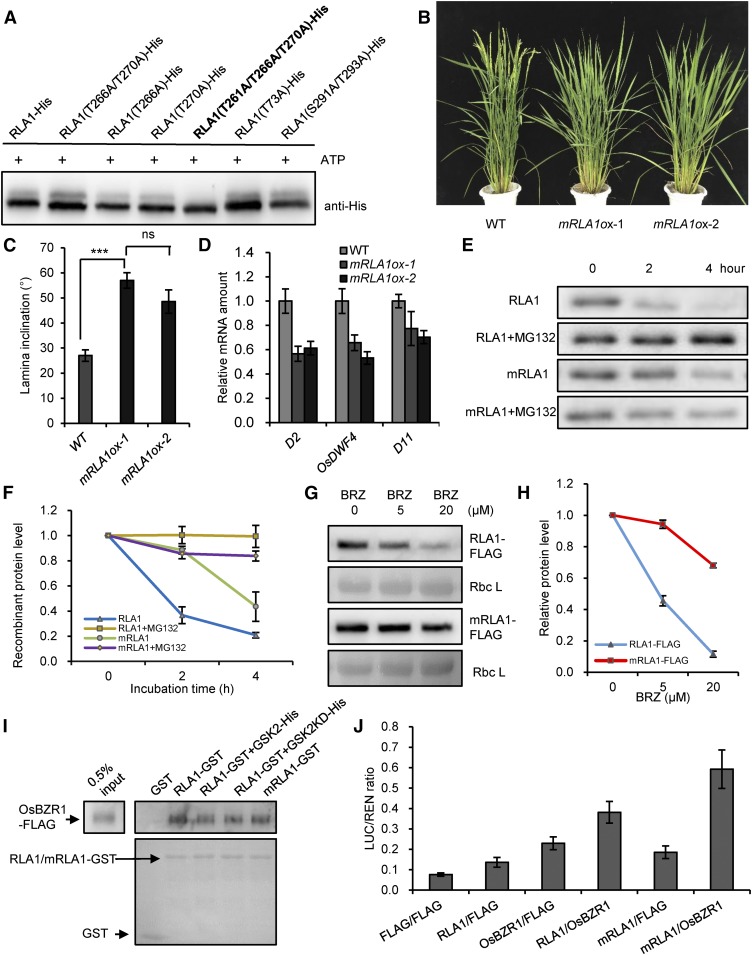
Figure 8.
BRs Regulate the Stability of RLA1 Protein through Phosphorylation by GSK2.
(A) GSK2 mainly phosphorylates RLA1 on Thr-261, Thr-266, and Thr-270. An equal amount of recombinant proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and detected by anti-His antibody. The phosphorylated sites are highlighted with bold font.
(B) Phenotypes of the mRLA1ox (T261A/T266A/T270A) transgenic plants.
(C) The statistical data of the lamina angle of the second lamina joint of plants from (B). Data are means ± se (n = 20). The comparisons were determined by Student’s t test. ***P < 0.001, and “ns” means no significance.
(D) The transcript levels of D2, OsDWF4, and D11 in plants of (B). The transcript level in the wild type was defined as “1.” Data are means ± se (n = 3).
(E) Time course of degradation of RLA1-His and mRLA1-His (T261A/T266A/T270A) in the wild-type plants. In vitro cell-free degradation assays were conducted.
(F) Quantification analysis for (E). The relative levels of RLA1-His or mRLA1-His incubated with wild-type plant protein extracts at 0 h were defined as “1.” Data are means ± se (n = 3).
(G) RLA1-FLAG or mRLA1-FLAG protein levels in the RLA1ox or mRLA1ox lines grown on medium containing BRZ for 8 d. Rbc L was used as a loading control.
(H) Quantification analysis for (G). The relative levels of the RLA1-FLAG/mRLA1-FLAG grown on 0 μM BRZ were defined as “1.” Data are means ± se (n = 3).
(I) Different proteins (RLA1-GST with GSK2 or GSK2-KD proteins, mRLA1-GST) can pull down OsBZR1-D-FLAG from total protein extracts of the Osbzr1-D-FLAG plants. RLA1-GST/mRLA1-GST and GST were stained with Ponceau S as loading controls.
(J) Transient gene expression assays in rice protoplasts. The LUC reporter gene was cotransfected with OsBZR1-FLAG, RLA1-FLAG/mRLA1-FLAG, or both. Data are means ± se (n = 3).