Figure 2.
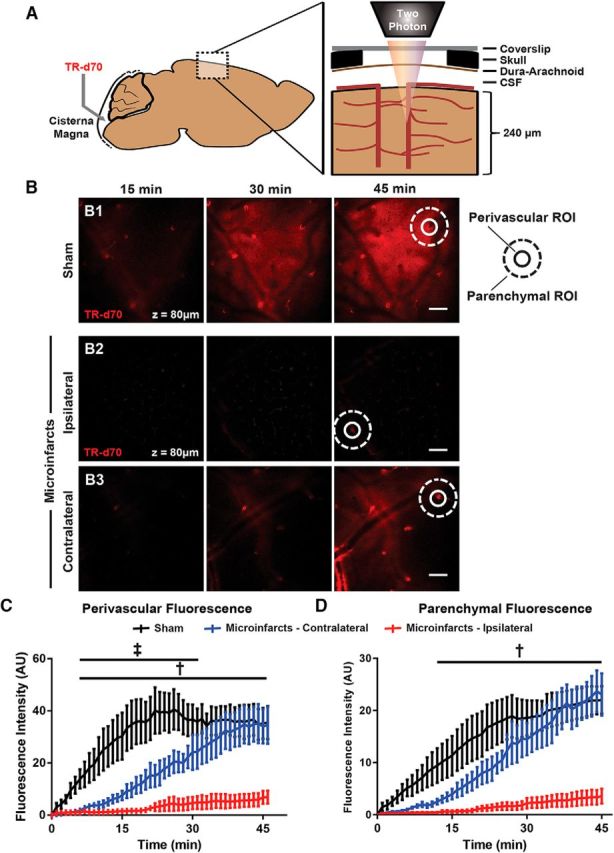
CSF tracer influx along the glymphatic pathway is reduced after multiple microinfarcts. A, Cortical influx of CSF tracer after intracisternal infusion was evaluated in vivo through a closed cranial window by two-photon microscopy. B, Representative imaging planes 120 μm below cortical surface 15, 30, and 45 min after intracisternal tracer infusion of sham-treated mice (B1) or those subjected to multiple microinfarcts and imaged over the ipsilateral (B2) or contralateral (B3) hemispheres 3 d after injury. Representative perivascular (circular) and parenchymal (donut-shaped) ROIs are shown. C, CSF tracer influx is dramatically slowed within both the ipsilateral and contralateral hemispheres (‡padj < 0.05 ipsilateral vs sham; †padj < 0.05 contralateral vs sham; n = 4 per group). D, CSF tracer movement through the surrounding parenchyma was slowed markedly after microinfarcts (†padj < 0.05 ipsliateral vs sham). Scale bars in B, 100 μm.
