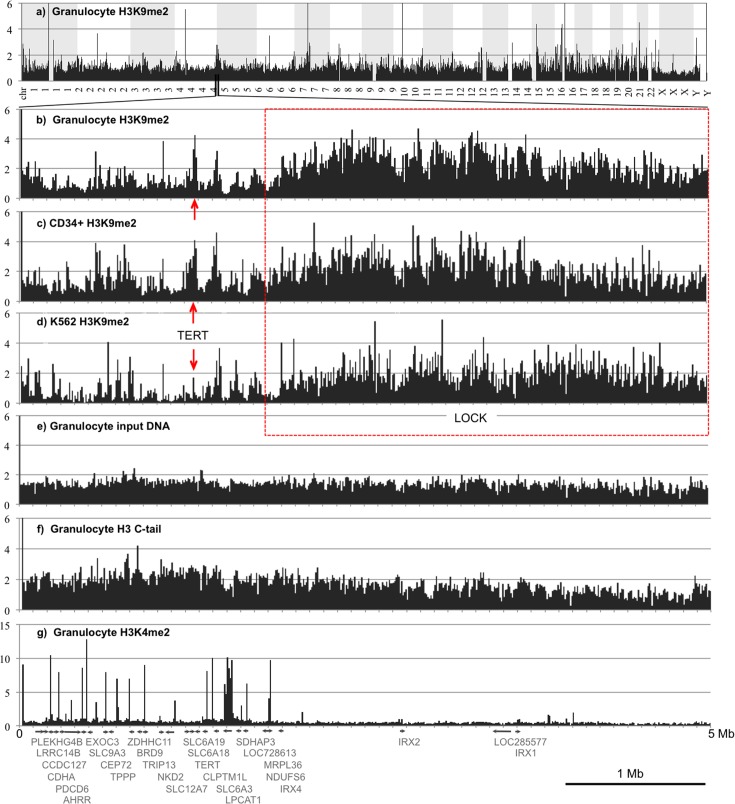
Fig 1. Human myeloid cells contain conserved blocks of H3K9me2 at gene-depleted chromosomal regions.
Distribution of DNA sequence reads mapped to the human genome at 1Mb resolution (a) and at 10 kb resolution (showing a region of chromosome 5 between 0 and 5 Mb (b-g). DNA sequence reads were derived from H3K9me2 ChIP-seq of granulocytes sample 15 (a, b), bone marrow CD34+ cells sample 20 (c), K562 cells sample 3 (d); granulocyte input DNA sample 23 (e), granulocyte ChIP-seq of H3 C-tail sample 16 (f), and granulocyte ChIP-seq of H3K4me2 sample 28 (g). The reads were grouped by 10 kb windows and normalized to genome average over the total human genome. Note enrichment of H3K9me2 over a large chromosomal domain, or LOCK [18] indicated by red dashed line box and variable levels of H3K9me2 over the TERT gene forming a peak in the granulocyte and CD34+ cells but not in K562 cells indicated by vertical red arrows. Y-axes represent fold enrichment of sequence reads vs. genome average.