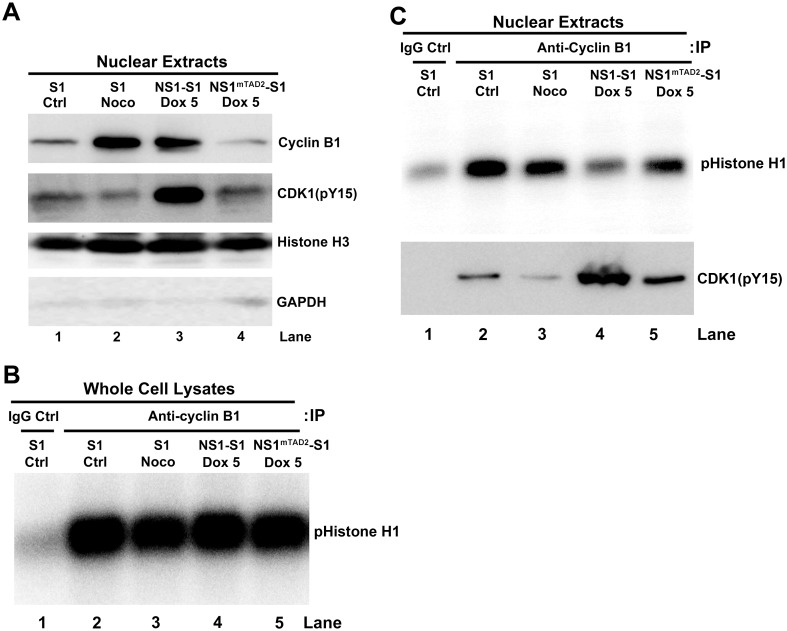
Fig 4. NS1 does not block the cyclin B1/CDK1 complex from entering the nucleus but it does inhibit its kinase activity.
(A) Western blot analysis. NS1-S1 and NS1mTAD2-S1 cells were treated with Dox for 72 h, collected, and lysed, and the nuclei were extracted. Western blot analysis was then performed to detect cyclin B1 and phosphorylated CDK1(pY15), as well as nuclear histone H3 and cytoplasmic GAPDH (Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase). Nuclear extracts from S1 cells and S1 cells treated with nocodazole (Noco) were loaded as controls. (B&C) In vitro CDK1 kinase assay. Equivalent amounts of proteins derived from whole cell lysate (B) or nuclear extracts (C) from S1 cells, S1 cells treated with Noco, and Dox-induced NS1-S1 and NS1mTAD2-S1 cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-cyclin B1-crosslinked protein A/G Plus agarose beads for in vitro CDK1 kinase assay. The final products were resolved on a 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel. The gel was then dried prior to autoradiography, and the phosphorylated histone H1 (pHistone H1) is indicated. (C) Lower panel: Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) of cyclin B1 and CDK1(pY15) in the nuclear extracts. Nuclear extracts prepared from S1, S1/Noco, NS1-S1/Dox+, and NS1mTAD2-S1/Dox+ cells were immunoprecipitated with an anti-cyclin B1 antibody. The eluted proteins were analyzed for CDK1(pY15) by Western blotting. Normal mouse IgG (IgG Ctrl) was used as negative control of immunoprecipitation of control S1 cell extracts.