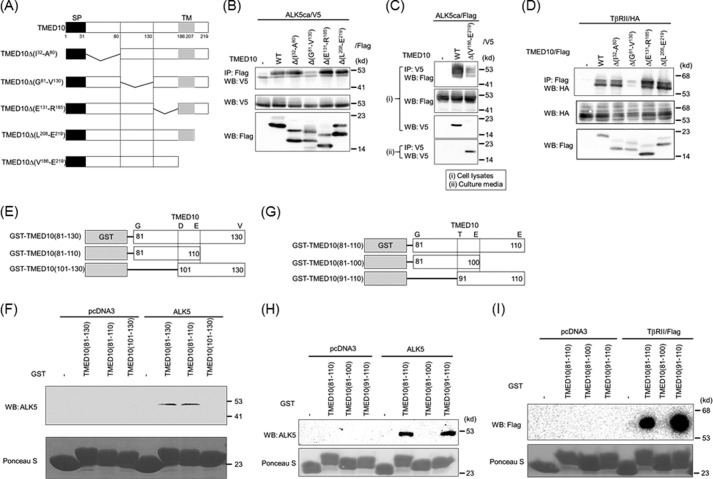
FIGURE 5.
Determination of the TGF-β receptor-interacting domain in TMED10. A, illustration of TMED10 and its mutants. SP, signal peptide; TM, transmembrane. B, interaction of TMED10 or its mutants with ALK5. COS7 cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids and harvested for co-IP experiments. The interaction between ALK5 and either TMED10 or its mutants is shown in the top panel. Total expressions of ALK5ca/V5 and TMED10/FLAG (or its mutants) are shown in the middle and bottom panel, respectively. C, non-necessity of both the transmembrane and the intracellular domains of TMED10 to interact with ALK5. The COS7 cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids. Section I, after cell lysis, anti-V5 antibodies were used for immunoprecipitation. The immunoprecipitates were separated by SDS-PAGE followed by Western blotting analysis (WB) using anti-FLAG antibody to detect their interaction (top panel). Total expressions of ALK5ca/FLAG and TMED10/V5 (or its mutants) in cells are shown in the second and third panel, respectively. Section II, because TMED10Δ(V186-E219) seemed to be a secretory protein, immunoprecipitation of TMED10Δ(V186-E219) into the media in which the cells were cultured was performed to detect secretory TMED10Δ(V186-E219) (bottom panel). D, interaction of TMED10 or its mutants with TβRII. Co-IP was performed as described in B above. The interaction between TβRII and TMED10 or it mutants is shown in the top panel. Total expressions of TβRII and TMED10 or its mutants were detected using anti-HA12CA5 (middle panel) and anti-FLAG antibodies (bottom panel), respectively. E, schematic presentation of GST-TMED10 fusion proteins. The region from Gly81 to Val130 in TMED10 was split into two pieces to make GST fusion proteins. F, requirement of the region consisting of 30 amino acids from Gly81 to Glu110 within TMED10 to interact with ALK5. A GST pulldown assay was performed using the GST fusion proteins described in E above. ALK5 ectopically expressed in COS7 cells was mixed with GST fusion protein. After loading the protein(s) bound to GSH-Sepharose 4B in SDS-PAGE, Western blotting analysis was performed using anti-ALK5 (V-22) antibody (top panel). The cell lysates from COS7 cells transfected with pcDNA3 were used as the negative control. As loading controls, GST and GST fusion proteins were visible with Ponceau S staining (bottom panel). G, illustration of GST-TMED10 fusion proteins. The region from Gly81 to Glu110 in TMED10 was divided into two pieces to make GST fusion proteins. H, determination of the ALK5-binding region in TMED10. A GST pulldown assay was carried out as described in F above. The top and bottom panels show the interaction of ALK5 with GST fusion proteins and the loading controls with Ponceau S staining. I, requirement of a 20-amino acid-long region in TMED10 to associate with TβRII. A GST pulldown assay was carried out as described in F above. The upper and lower panels show the interaction of TβRII with GST fusion proteins and the loading controls with Ponceau S staining.