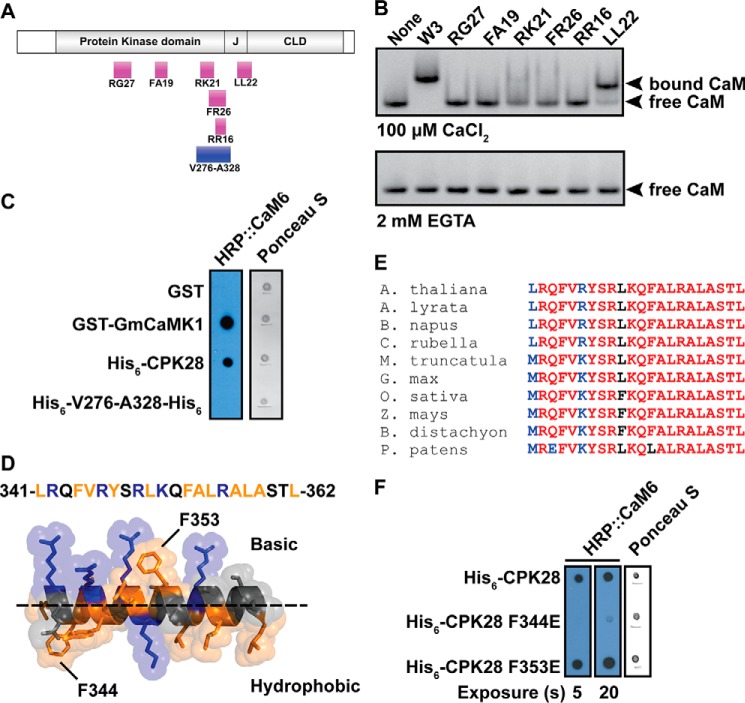
FIGURE 4.
CaM binds to a peptide from the CPK28 junction domain. A, schematic map of the domain organization of CPK28 showing the location of peptides (magenta boxes) and recombinant proteins (blue boxes) used to delineate the CaM-binding domain. B, peptide binding by CaM6 in native PAGE in the presence (100 μm CaCl2) or absence (2 mm EGTA) of Ca2+ as indicated. CaM-peptide complexes were visualized by staining with GelCode Blue protein stain after electrophoresis. C, overlay assay indicating lack of binding to a C-terminal fragment (Val-276 to Ala-328) of the CPK28 kinase domain. Proteins were spotted to nitrocellulose membrane and probed with 200 nm HRP::CaM6. Full-length CPK28 was detected by HRP::CaM6 but the Val-276 to Ala-328 fragment was not. D, helical model of the LL22 peptide rendered in PyMOL. Basic residues are shown in blue, and hydrophobic residues are shown in orange. Basic and hydrophobic faces of the amphipathic helix are indicated (above and below the dashed line, respectively). Potential hydrophobic anchor residues are indicated. E, HRP::CaM6 overlay analysis of CaM binding to CPK28 CaMBD mutants. Approximately 400 ng of each protein was spotted, and the blot was probed with 100 nm HRP::CaM6. CaMBD, CaM-binding domain; HRP, horseradish peroxidase. F, Clustal-Omega alignment of the CPK28 CaM-binding domain with the corresponding region from other species. The CaM-binding domain is highly conserved across diverse plant taxa. GenBankTM accession numbers for sequences used for the alignment are: Arabidopsis lyrata, XP_002865081.1; Brassica napus, XP_013653730.1; Capsela rubella, XP_006282144.1; Medicago truncatula, XP_003612167.1; Glycine max, XP_003538879.1; Oryza sativa, NP_001059444.1; Zea mays, NP_001151048.1; Brachypodium distachyon, XP_003557300.1; Physcomitrella patens, XP_001766209.1.