Figure 7. FIGURE 7: Diagrammatic summary of the effect of loss of btn1 on the response to stress.
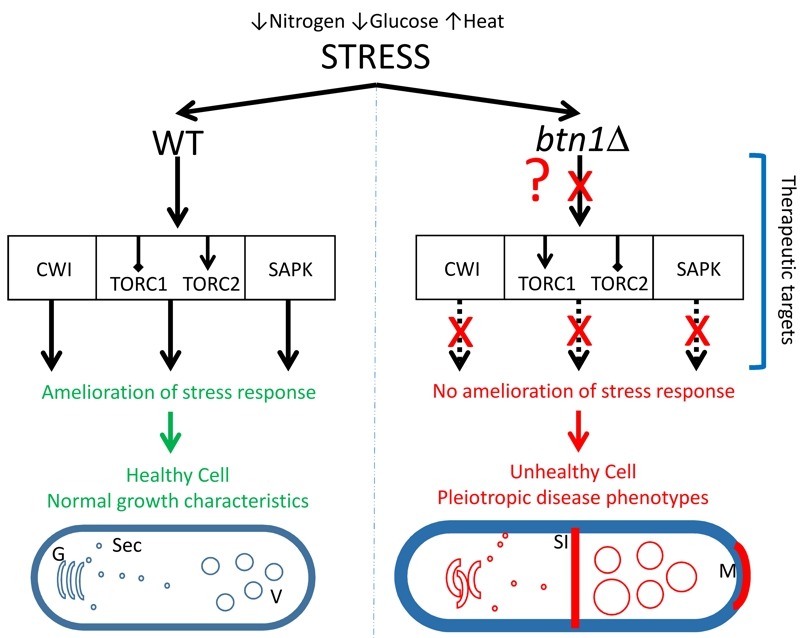
The left panel shows the response of healthy cells to stresses applied in this study, such as low nitrogen or glucose or raised temperature. These cells are able to respond via interconnected signaling pathways such as CWI, TORC and SAPK. Activation of these pathways allows the cell to respond to the effects of stress and restore cell homeostasis and integrity. In contrast, cells lacking btn1 are unable to respond to the applied stresses (represented by ‘?’ and ‘X’) and undergo a variety of previously reported responses that include an increase in vacuole size, swollen and disorganized Golgi and mis-trafficking of vacuole enzymes such as carboxypeptidase Y, increased septation index and longer cell cycle and cell length, monopolar growth, defective cell wall, absence of cell rounding (in response to low glucose). Genetic or pharmacological activation of the three signalling pathway provides partial or full rescue of these pleiotropic phenotypes of btn1Δ cells. G, Golgi; Sec, secretory vesicles; V, vacuole; SI, division septum; M, monopolar growth.
