Figure 2. IRISOE promotes expression of EMT-inducers and stemness-enforcers in breast cancers.
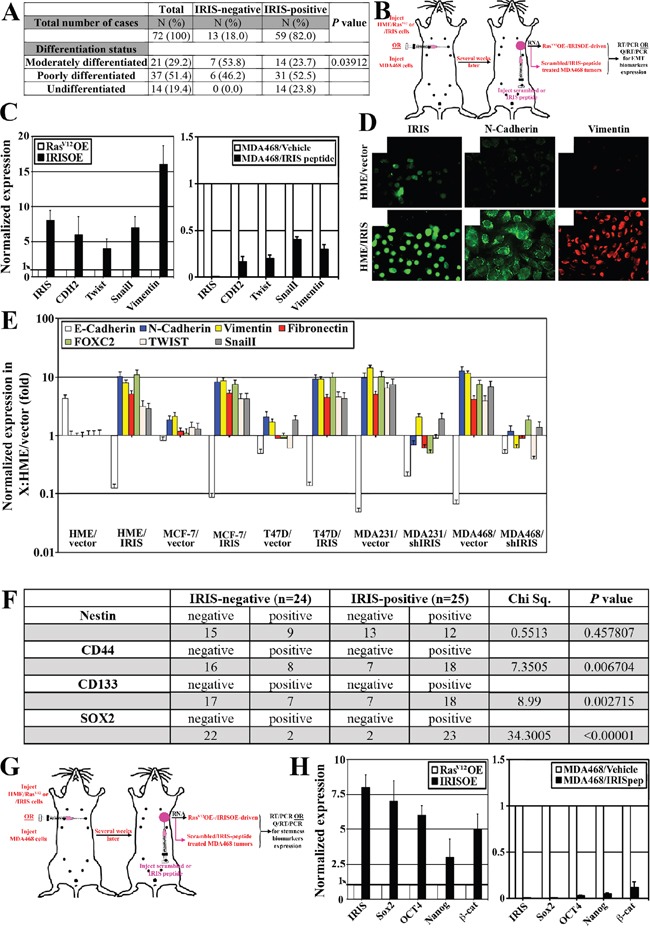
A. Association analysis between IRIS expression and the differentiation status of TNBC tumors (n=72). B. Schematic of the strategy used to generate RasV12OE-/IRISOE-driven or MDA468 + scrambled/MDA468 + IRIS inhibitory peptide orthotopic mammary tumors in SCID/Nu/Nu mice, followed by tumor and RNA isolation and EMT-inducers expression analysis. C. Real-time QRT/PCR analysis showing the expression of IRIS and several EMT-inducers mRNAs in RasV12OE-driven or IRISOE-driven orthotopic mammary tumors (left), and MDA468 orthotopic mammary tumors after treatment with scrambled- or IRIS-inhibitory peptide (right), generated as in (B). D. Immunofluorescence analysis of IRIS, N-cadherin and vimentin expression in naïve (uppers) or IRISOE (lowers) HME cells. E. Real time QRT/PCR of indicated mRNAs in naïve/IRISOE HME cells, vector/IRIS transfected MCF7 or T47D, and shcontrol/shIRIS transfected MDA231 or MDA468. F. Association analysis between IRISOE and the expression of several TIC-biomarkers in a cohort of locally advanced breast cancer patients (n=49, from Egyptian NCI) conducted using real-time QRT/PCR. G. Schematic of the strategy used to generate RasV12OE-/IRISOE-driven or MDA468 + scrambled/MDA468 + IRIS inhibitory peptide orthotopic mammary tumors in SCID/Nu/Nu mice, followed by tumor and RNA isolation and stemness-enforcers expression analysis. H. Real-time QRT/PCR analysis for the expression of IRIS and the stemness-enforcers mRNAs expression in RasV12OE-driven or IRISOE-driven orthotopic mammary tumors (left), and MDA468 orthotopic mammary tumors after treatment with scrambled- or IRIS-inhibitory peptide (right), generated as (G).
