Figure 1. Schematics of Wnt signaling pathways in cancer cells.
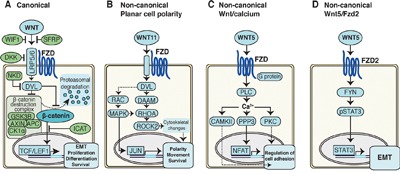
A. Canonical Wnt pathway. In the absence of Wnt signaling, the β-catenin destruction complex labels β-catenin for proteasomal degradation. In the presence of Wnt signaling, the destruction complex is inhibited, resulting in stabilization and nuclear translocation of β-catenin, activating transcription of target genes. B. Non-canonical planar cell polarity (PCP) pathway activates signaling cascades resulting in cytoskeletal changes, as well as alterations in cell polarity, movement and survival. C. Non-canonical Wnt/Calcium pathway signaling activates intracellular calcium, which in turn reduce cell adhesion through further signaling. D. Non-canonical Wnt5/Fzd2 pathway. Wnt5 signals via the FZD2 receptor and FYN activates STAT3 transcription leading to epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in cancer cells.
