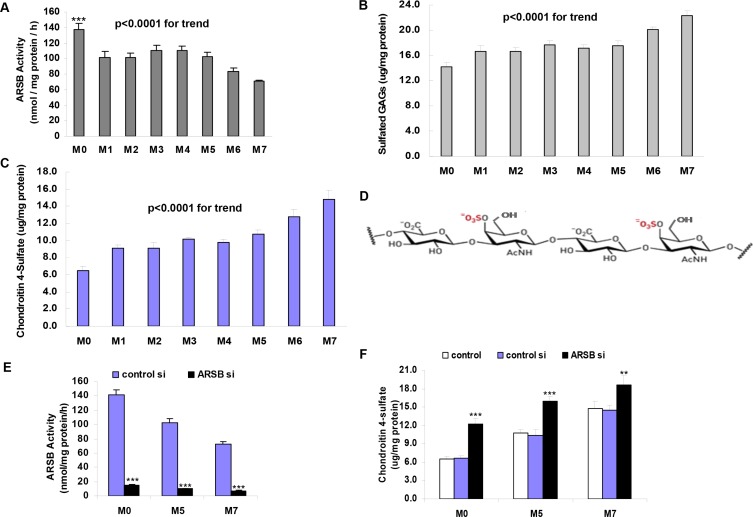
Figure 1. Decline in ARSB activity and increase in total sulfated glycosaminoglycans and C4S with increasing aggressiveness of melanoma cell lines.
(A) ARSB activity is significantly higher in the normal human melanocytes (M0; PCS-200-013, ATCC) than in the malignant cell lines ([WM1552C (M1), WM1552C/mock (mock CSPG4 transfection) (M2), WM1552C/MCSP (CSPG4 transfected) (M3), WM1552C/MCSPΔCD (transfected with CSPG4 without the cytoplasmic domain) (M4), WM35 (M5)], WM1341D (M6) and from metastatic melanoma (1205 Lu) (M7) (p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA with Tukey-Kramer post-test; n = 3). (B) Total sulfated glycosaminoglycans are greater in the more aggressive melanoma cell lines (p < 0.0001 for trend; n = 3). (C) Chondroitin 4-sulfate is significantly greater in the more aggressive melanoma cell lines, and the levels increase as the cell lines are increasingly aggressive (p < 0.0001 for trend; n = 3). (D) The structure of chondroitin 4-sulfate (C4S) shows: the presence of the 4-sulfate group of N-acetylgalactosamine; alternating beta-1, 3 and beta-1, 4 glycosidic bonds; and the fundamental disaccharide unit consisting of N-acetylgalactosamine 4-sulfate and glucuronate. (E) When ARSB is silenced by siRNA, the activity in the M0 cells declines to about 10% of the baseline level. Values in the M5 cells in the radial growth phase are intermediate between the values in the normal melanocytes (M0) and the values in the metastatic melanoma cell line (M7) (n = 3). (F) When ARSB is silenced by siRNA, the C4S level increases significantly in the three cell lines (p < 0.001; n = 3). [AcNH=N-acetyl; ARSB=arylsulfatase B; C4S=chondroitin 4-sulfate; GAG=glycosaminoglycan; si=siRNA=small interfering RNA].