Figure 2. A highly conserved minimal promoter at the ARHGEF2 transcription start site drives luciferase expression.
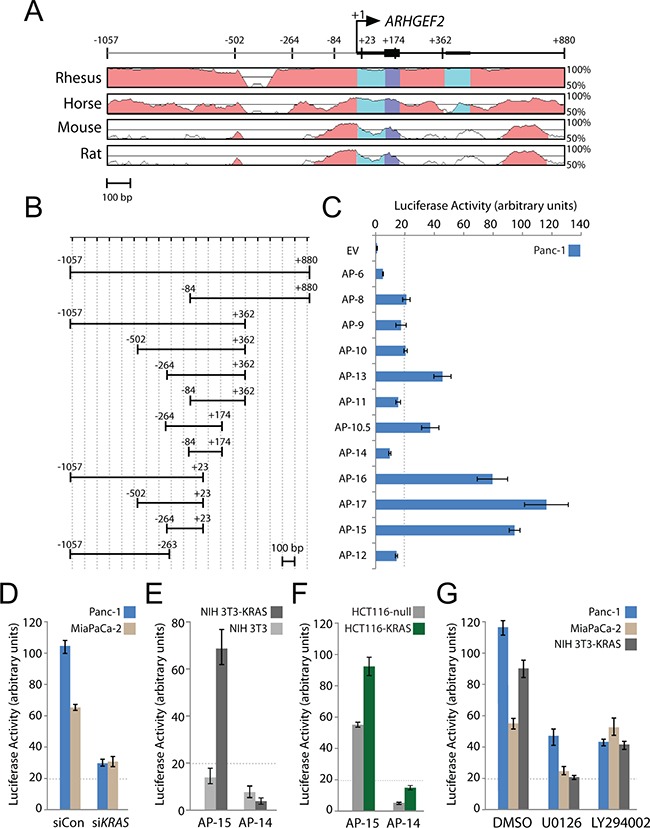
A. Phylogenetic conservation of the genomic region around the transcription start site (TSS) of ARHGEF2. VISTA (http://genome.lbl.gov/vista/index.shtml) was used to generate pairwise alignments between the human ARHGEF2 sequence and homologous sequences in the indicated species. Graphs illustrate nucleotide identity for a 100 bp sliding window centered at a given position. Position +1 of ARHGEF2 mRNA and the positions of the boundaries of promoter constructs used in panel B are mapped. B. Boundaries of ARHGEF2 promoter constructs cloned into the pGL3-basic luciferase reporter vector. Numbers are relative to the TSS. Scale bar is 100 base pairs (bp). C. Normalized luciferase activity generated from the indicated ARHGEF2 promoter (AP) construct transfected in Panc-1 cells. Luciferase activity was normalized to renilla expression and data is plotted as the fold change over cells expressing pGL3-promoterless empty vector (EV). Error bars in this and subsequent experiments represent standard deviations from three independent transfections. Luciferase expression below the dotted line was considered insignificant. D. Normalized luciferase activity from AP-15 promoter construct in a Panc-1 and MiaPaCa-2 cells pretreated with control siRNA (siCon) or siRNA targeting KRAS (siKRAS). E. Normalized luciferase activity from AP-15 and AP-14 promoter constructs in isogenic NIH-3T3 and NIH-3T3-KRAS cell lines. F. Normalized luciferase activity from AP-15 and AP-14 ARHGEF2 promoter constructs in isogenic HCT116-null and HCT116-KRAS cell lines. G. Normalized luciferase activity from AP-15 promoter construct in the indicated cell lines pretreated with DMSO, 10μM U0126 or 5μM LY294002.
