Extended Data Figure 8. Distinguishing features of cervical cancer integrated molecular subtypes.
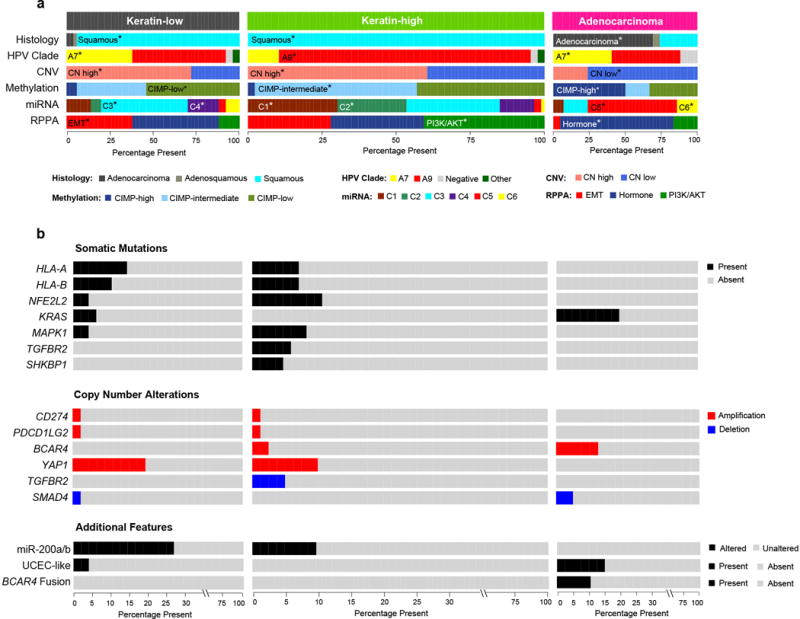
a, Integrative clustering of 178 cervical cancer Core Set cases using mRNA, methylation, miRNA, and copy number data identified three iClusters: (i) Keratin-low, (ii) Keratin-high, and (iii) Adenocarcinoma-rich (Adenocarcinoma; top feature bar). Relative frequencies of various cervical cancer classifications defined by histology, HPV clade, copy number variation (CNV), methylation, miRNA, and RPPA are plotted. The color key for each feature is presented at the bottom. For each category, the statistically significantly enriched features in each iCluster (chi-squared test; p<0.05) are highlighted with asterisks and a listing of the name of the enriched feature. The width of each plot is scaled according to the number of samples within each cluster. b, The frequencies of somatic alterations and additional novel features that distinguish the iClusters, specifically those that do not occur in all three iClusters, are plotted. The “Somatic Mutations” panel shows the presence/absence of mutations for 7 of the identified significantly mutated genes. The “Copy Number Alterations” panel shows select copy number alterations (high level amplifications and focal deletions) that are differentially present across the iClusters. The “Additional Features” panel highlights miscellaneous features that also distinguish the iClusters, including the presence of miR-200a/b alterations, UCEC-like cases, and BCAR4 fusion events. The color key for each feature is present to the right of the plots.
