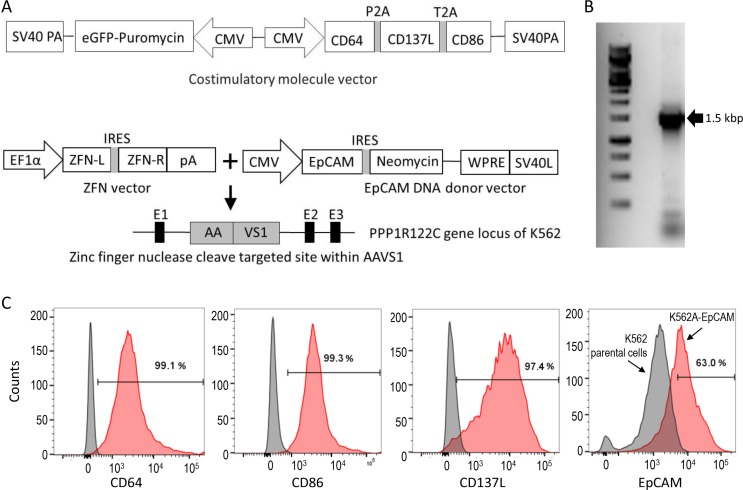
Figure 1. Preparation of a K562 aAPC line for expansion of anti-EpCAM CAR-expressing T cells.
(A) Schematic diagrams of plasmid vectors used for the generation of the aAPC cell line. The costimulatory molecule vector (top) was used for transfection of wild-type K562 cells to generate puromycin-resistant K562 cells expressing CD64, CD137L and CD86 (K562A). K562A cells were further modified by co-transfection with the ZFN vector and EpCAM DNA donor vector (bottom) for AAVS1 locus-specific gene insertion to generate puromycin- and neomycin-resistant aAPCs expressing EpCAM (K562A-EpCAM). (B) PCR genome typing to demonstrate the AAVS1 locus-specific gene insertion of the EpCAM gene, as indicated by the presence of one single 1.5-kb band. (C) Phenotype analysis of K562A-EpCAM cells. Flow cytometric analysis demonstrates the surface expression of CD64, CD86, CD137L, and EpCAM. In the panels for CD64, CD86, and CD137L, left curves: isotype controls; right curves: antibodies. In the panel for EpCAM, left curve: K562 parental cells; right curve: K562A-EpCAM cells.