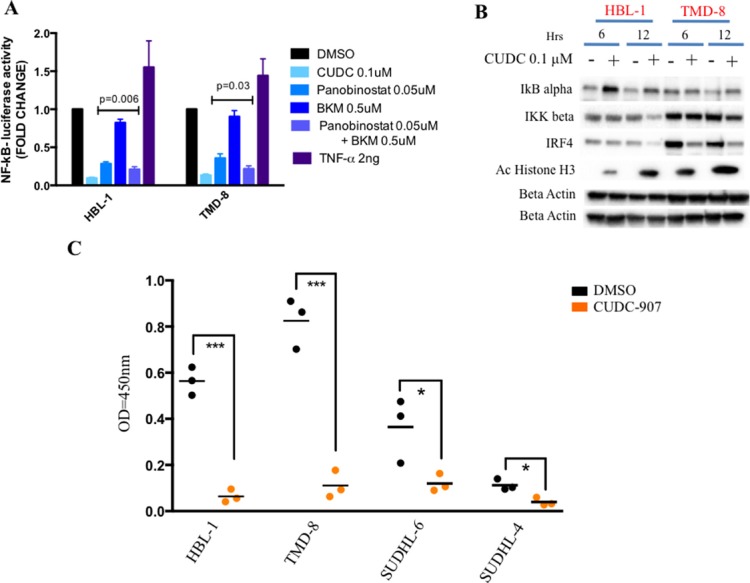
Figure 4. CUDC-907 inhibits NF-kB signaling in ABC DLBCLs.
(A) Relative NF-kB-luciferase activity in two representative ABC DLBCL cell lines (HBL-1 and TMD-8). Cells were treated for 12 hours with indicated concentration of either panobinostat, BKM-120, the combination of these two drugs, CUDC-907 or DMSO. Cells were incubated with 2 ng of TNF-α as positive control for NF-kB activation. Error bars represent standard error of the mean (S.E.M) of triplicate experiments. (B) Western blot demonstrating that CUDC-907 (0.1 μM for 6 and 12 hours) inhibits NF-kB activation by increasing IkB alpha levels and decreasing IKK beta levels in two representative ABC DLBCL cell lines (HBL-1 and TMD-8). The changes were associated with a decrease in IRF4 levels (see Supplementary Figure 2B). (C) ELISA assay showing a more pronounced decrease of nuclear NF-kB p65 in two representative ABC (HBL-1 and TMD-8) cell lines compared with two GCB (SUDHL-6 and SUDHL-4) treated with either 0.1 μM CUDC-907 or DMSO for 12 hours. Differences between groups were calculated with the Student's t test. *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001.