Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the general structure of the excitatory synapses.
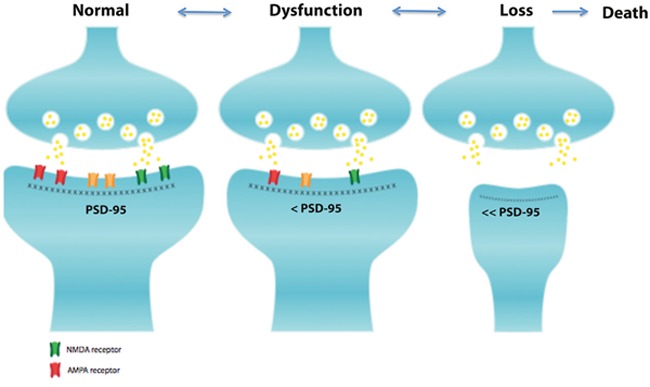
Excitatory synapses are composed by the pre- and post-synaptic elements. In the post-synaptic element there is a specialization of the cell membrane called the postsynaptic density region (PSD), this zone contains a large number of scaffolding proteins. Among these proteins, PSD-95 is the more abundant and plays an important role in the localization of AMPA (red channels) and NMDA (green channel) receptors. Slight perturbations of the spine architecture lead to spine dysfunction and subsequently loss. The mechanism underling synaptic dysfunction is characterized by an initial reversible stage with a slight reduction of PSD-95 protein, NMDA and AMPA receptors that induces a synaptic dysfunction. Afterwards, a major decrease of PSD-95 occurs inducing an atrophy of the post-synaptic element that generate synaptic loss and eventually neuronal death.
